From an anatomical point of view, the elbow joint is a complex biomechanism that consists of many parts. It is formed by the humerus, radius and ulna, a large number of nerves and blood vessels. Due to the complex structure of the fracture elbow joint most often accompanied by complications. This kind of injury can only be healed by surgical intervention, moreover, repeatedly.
From the statistics it follows that 20% of fractures occur precisely in the elbow region. Such injuries are classified as severe and complex and are divided into: periarticular and intraarticular, closed and open. In addition, a fracture can be combined with a dislocation.
The most common cause is weakness of the elbow tendons and ligaments. Well stretched tendons are the main prevention of such injuries.
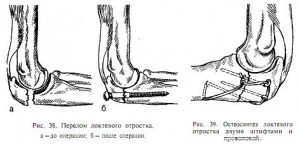
The first blow, as a rule, receives the olecranon, which does not have a muscular frame. However, it rarely breaks (0.85 - 1.5%). This injury is accompanied by detachment or displacement of fragments, which additionally injures blood vessels, ligaments and nerves.
Fault radius or cervical is possible when a person falls on an outstretched hand. These types of injuries are divided into fractures:
- no offset;
- marginal with offset;
- fragmented.
The coronoid process rarely breaks, but is combined with forearm injuries, dislocations, and displacement of fragments. Most often breaks the proximal ends of the bones of the forearm and the distal ends humerus.
In children and adolescents, severe injuries to the external or internal humerus are most common, along with displacement of the internal epicondyle. In this case, between humerus and the olecranon can pinch broken-off bone fragments.
Symptoms:
- sharp pain in the elbow and forearm, which can also spread to the wrist and fingers;
- significant limitation or impossibility of movements;
- mobility that is not characteristic of normal functioning, for example, pathological lateral mobility;
- edema and non-merthrosis, accompanied by severe hematoma;
- at open fracture as a result of damage to the muscles, blood vessels, nerves and skin, bleeding and gaping of the bones may occur.
Diagnostics:
- palpation along the line of injury to feel the fragments;
- trying to bend the forearm to see if it causes pain (if the fracture is not displaced, the movements are only limited);
- x-ray in direct and lateral projection;
- intra-articular fracture requires computed tomography.
Treatment
 The choice of treatment tactics depends on the degree of violation of the structure of the joint. The very first is immobilization, which can be of two types:
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the degree of violation of the structure of the joint. The very first is immobilization, which can be of two types:
- pre-hospital (first aid) - splinting;
- stationary (after diagnosis) - the imposition of a plaster splint.
Before applying plaster, it is most often necessary to restore the structure of the joint (in case of displacement) or a surgical operation, which is accompanied by fastening the bones with the help of special screws, knitting needles or other devices. If the head of the bone is severely damaged, it is replaced with an endoprosthesis.
A plaster splint is applied for four weeks. Then it must be worn for another week, periodically taking off for 15 - 20 minutes in order to develop movements - bend and unbend the arm at the elbow several times.
With a periarticular fracture of the ulnar region without fragments, it is indicated conservative treatment. Immobilization is carried out using a hinged orthosis. All rehabilitation activities are required.
If surgery is necessary, the joint must be immobilized at an angle of 30 to 60 degrees before surgery and drug treatment aimed at reducing edema and reducing hematoma. With an open fracture, the operation should be performed within the first days after the injury. After surgery, it is mandatory to apply all the points of the rehabilitation program.
Venous drainage can be improved by elevated position of the elbow joint. This also reduces swelling and hematoma.
Rehabilitation activities
During immobilization, ligaments and tendons have time to atrophy. After removing the plaster, it is immediately prescribed physiotherapy, physiotherapy and water procedures. Their goal is to restore mobility. Rehabilitation can take from two weeks to one and a half months. The duration depends on the type of injury.
The development of the elbow joint after a fracture occurs in three periods:
First period
consists of two stages:
- during immobilization begin breathing exercises and exercises for shoulder joint and fingers to reduce swelling and pain
- a broken arm is placed behind the head on a pillow to strain the muscles of the shoulder and forearm;
Second phase
begins after the removal of the cast and includes gentle flexion and extension of the arm at the elbow.
The second period consists of the following exercises:
- the patient sits, the hand is located on the table, in this position the hand bends and unbends;
- exercises are performed with a stick or ball in a sitting or standing position;
- flexion and extension at the same time of the diseased and healthy arm at the elbow by lifting it behind the head, holding the arms together in the lock;
- exercise in a bath with warm water;
In the third period
- a transition to pronation and supination in water is carried out, which is supplemented by physiotherapeutic procedures (paraffin, mud, currents, ozocerite) and drug treatment.
The number of repetitions of any exercise is five times. But classes should be held several times a day. A sick hand should not get tired.
 In the first period of rehabilitation, massage is contraindicated. In the second and third periods, you can massage the back and massage the hands above and below the damaged area. In the third period, sparing procedures begin, aimed at restoring motor functions, resorption of the hematoma, preventing muscle atrophy and strengthening the ligaments.
In the first period of rehabilitation, massage is contraindicated. In the second and third periods, you can massage the back and massage the hands above and below the damaged area. In the third period, sparing procedures begin, aimed at restoring motor functions, resorption of the hematoma, preventing muscle atrophy and strengthening the ligaments.
During rehabilitation, it is contraindicated to carry weights, stops, muscle fatigue, hanging, movements, causing pain, leading to reflex muscle contractions and proliferation of bone deformities in the form of "whiskers" or "spurs".
Prevention of elbow injuries
Injuries and illnesses are much easier to prevent than to treat. To prevent fractures in the elbow area, it is necessary to strengthen and nourish the ligaments. This requires exercises:
- in a standing position, pick up dumbbells and lift until the elbow is bent at an angle of 90 degrees, return to the starting position;
- take dumbbells, raise them to the biceps and hold as much as possible;
- take push-up positions and hold the body in this position for as long as possible.
To strengthen the ligaments, not only exercises are important, but also the diet. It should include vitamins C and E, as well as collagen. Vitamin C contains regular and cauliflower, tomatoes, sweet peppers, green pea, lettuce, spinach, parsley, blackcurrant, gooseberry, rosehip, kiwi and citrus fruits. Vitamin E contains cereal grains, lettuce, carrots, beets, celery, parsley, garlic, sea buckthorn, pumpkin seeds, vegetable oils, egg yolks, rose hip.
To replenish the body's reserves of collagen, you should consume:
- meat, especially turkey;
- fish, especially salmon;
- seaweed;
- oysters;
- oatmeal, barley, buckwheat, peas, beans.
The main goal of the diet is weight loss. Excess weight puts additional stress on all joints, which impairs metabolic processes in them. If the menu contains an excess of one component (for example, fats) and a lack of others, the condition of all tendons and ligaments worsens.
Hand injuries, especially those occurring inside the joint, are dangerous, and approximately 20% of them occur at the elbow. The elbow joint is one of the most complex in the human skeleton, since it combines three bones at once: the humerus, ulna and radius. In addition, it consists of a large number of small articular joints. All this is combined into a single elbow by connective tissues (muscles, ligaments).
The mobility of the limb is carried out due to the dynamics of the joint, as well as the vessels and nerve endings passing through the elbow. A fracture of the elbow joint is a serious injury, as it is often complicated by numerous consequences. In terms of severity, only a damaged knee can compete with it, since they are similar in structure. Treatment after a fracture will take a long time, the recovery period is even longer. Sometimes it is almost impossible to restore the mobility of the arm completely.
Causes of damage
There are many risk factors that can cause an elbow fracture. Among them there are the most frequent, due to which damage occurs:
- Unfortunate fall. A person tends to protect himself with his hands when falling, exposing them in front of him. fracture ulna- not an exception. Having fallen on an arm extended or half-bent at the elbow, a person receives the main blow precisely on the elbow joint. In other words, by putting forward hands, a person takes most of the damage on them.
- Chronic diseases. Bone fragility develops as a result of a series of chronic diseases, because of which it is almost impossible to warn against a fracture of the elbow joint. These diseases include osteoporosis, arthritis and many others that purposefully or indirectly destroy the bone structure. Exercise stress or the force of impact on the affected bone easily destroys it.
- Physical hits. A blow to the elbow can be received in a fight, a traffic accident, or simply by accidentally bumping into a door frame. Depending on how much force was applied and where the blow was directed, classified the complexity of the injury.
Much less often, injury occurs as a result of playing sports, since athletes pay special attention to equipment, and the elbow is usually protected. elastic bandage or a shield.
Elbow fracture classification
A fracture of the arm in the elbow joint is subdivided, like other fractures. Elbow fracture classification is defined as follows:
- closed or open;
- intraarticular or periarticular;
- with and without displacement (usually only one bone breaks);
- multiple, fragmented, etc.
A fracture of the ulna is often accompanied by a dislocation of the entire joint or stretching of the connective tissues and is complicated by many diseases, such as arthrosis.
As already mentioned, the elbow consists of three main bones and a large amount of muscle and connective tissue. In addition, the complexity of the elbow joint allows for a special classification according to the site of injury.
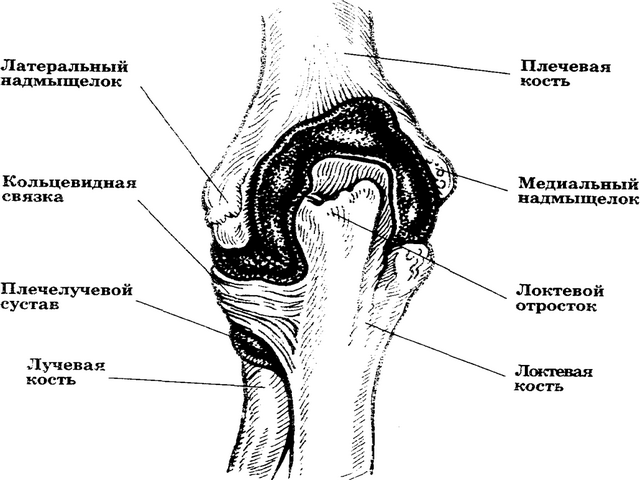
The olecranon is the weak point of the elbow. It is not closed, like the rest of the elbow, soft and muscle tissue. A direct fracture of the olecranon is a rather rare phenomenon, but in case of an unsuccessful fall, bone particles can break off from it. Such damage is greatly complicated by the displacement of fragments that damage blood vessels and muscle tissue.
Injury to the bone head or neck of the radius occurs as a result of a fall on an outstretched arm. This type of disorder is more common.
Violation of the coronoid process often occurs in combination with damage to the forearm and shoulder, or is accompanied by dislocation.
The most typical fracture for the radius, it may be accompanied by articular dislocation and damage to the humeral condyle.
Fracture symptoms
Diagnosing the main signs is quite simple - they are pronounced. A serious reason for applying for medical care at least one of the following symptoms will be present.
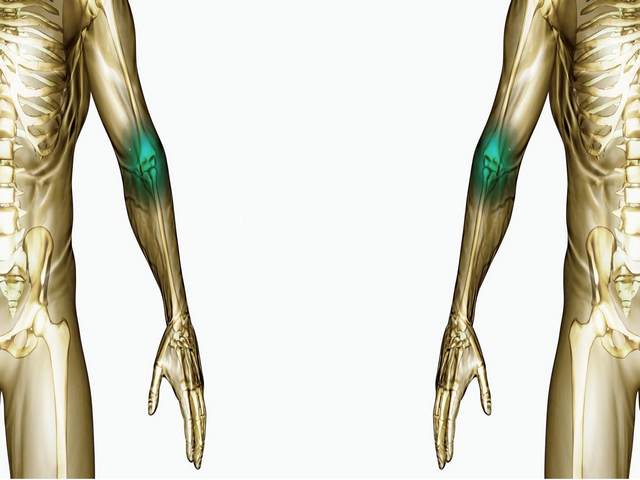
After an injury, the victim feels the following symptoms:
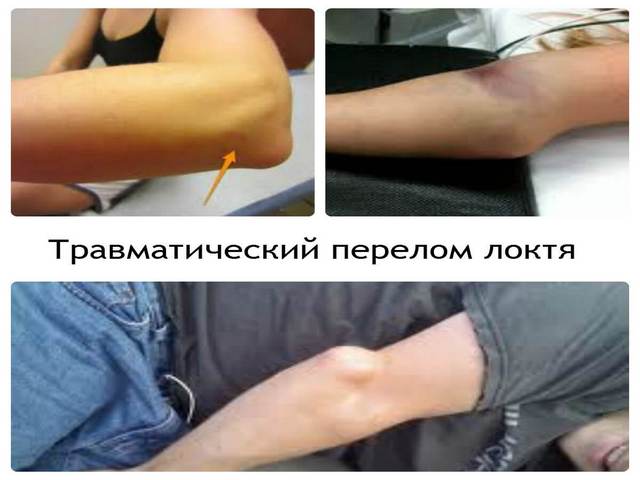
- the elbow joint swells strongly, the arm increases in size. The swelling is so extensive that it can be seen with the naked eye and without palpation - manual examination of the victim;
- the victim does not have the ability to move his arm, the elbow joint after damage is not able to move at all - a complex structure affects;
- an extensive hematoma quickly forms at the site of injury. Blood leaking into soft tissues after injury blood vessels tends to thicken over time and lead to unpleasant consequences. To remove such blood clots is possible only with the help of surgery;
- the strongest pain syndrome - the pain is strong, unbearable;
- crunching and visible deformation will be another cause for concern.
Displaced ulnar fractures are characterized by external signs: irregularities, pronounced bone positioning and inaccuracies instead of the usual structure of the hand.
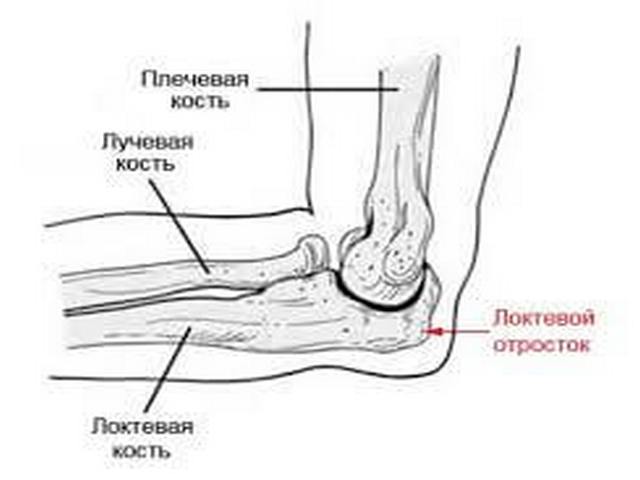
In more detail, the symptoms of trauma can be considered in individual cases:
- Olecranon injury is a very common hand injury, especially in childhood. Symptoms are slightly different from the main ones - pain is felt with inside joint, gives to the shoulder and forearm. Swelling and bruising spread along the outside of the joint. In addition, a fracture of the olecranon is assessed by whether it is possible to bend the arm at the elbow. In this case, rotational movements of the shoulders are possible. There is a characteristic crunch of bone fragments, as well as external deformities of the hand.
- A fracture of the head and neck of the radius is characterized by extensive pain in the front of the joint, radiating to the forearm. Hematomas and edema are not very pronounced, crunch and deformation are absent. A clear difference between such an injury and others is the restriction in rotational movements.
- Injury to the coronoid process of the elbow joint is described as severe aching pain, aggravated by palpation. It is practically impossible to move the joint itself to bend and unbend the arm. Insignificant edema is expressed by a slight swelling of the tissues over the joint, while there is no external deformation.
Thus, external disturbance hands and the crunch of bone fragments appears only if there has been a fracture of the entire elbow joint with displacement.
Urgent Care
Rendering first aid just necessary. In this case, the tactics of first aid should be selected according to the severity of the injury. However, it is reliable to establish the complexity of the injury, for example, when closed fracture does not seem possible. However, everyone should know the basics of first aid in order to help themselves or others in time.
The basics of pre-medical care fit into several of the following measures, which greatly simplify the course of the treatment period:
- The imposition of a homemade splint to immobilize the hand. It is necessary to firmly fix the hand on a solid object from the middle of the forearm to the fingertips. To do this, it must be tied to an impromptu tire (for example, a board) or tied to the body of the victim, if it is not possible to build a homemade splint.
Important! It is worth making sure that the injured arm is bent at a right angle.
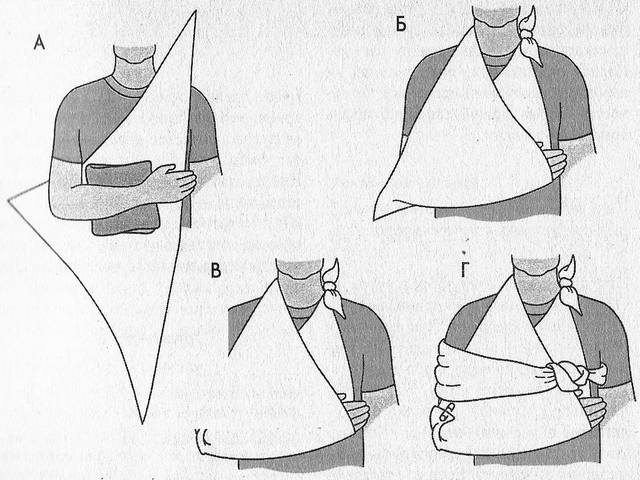
- For general pain relief, local anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Intramuscular administration of the drug will be more effective, but this is not always possible.
- If possible, apply cold to the injury. This will help reduce the swelling of the injury in order to make a diagnosis without complications. Ice will slightly reduce and general pain. Even an ordinary bottle of cold water or a frozen semi-finished product can play the role of ice.
Important! Dry ice or just a cold object must be wrapped in a soft cloth before being applied to the injury.
Diagnostics and therapeutic therapy
A traumatologist diagnoses an injury based on several x-rays. The elbow is photographed in several projections - this gives a more complete picture of the injury, also allowing you to establish possible consequences.
An elbow fracture is characterized by the fact that the edema increases over time. In the first week, the swelling increases. In the event that the fracture is closed, a tight plaster bandage is applied to the arm.
Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory complex drugs are used to relieve pain.
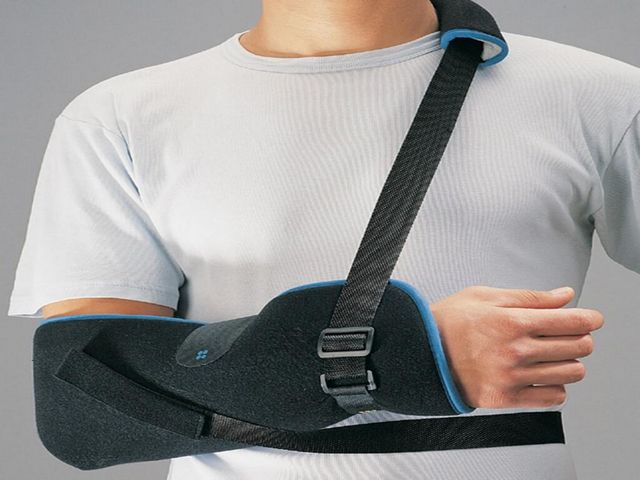
It is not recommended to load the injured arm for 3 weeks, after which the plaster is removed. In the future, it is necessary to develop the elbow joint, and for this, a rigid fixative is used, which replaces the plaster and does not interfere with movements.
The operation is allowed for open fractures with displacement. Moreover, such operations must be carried out immediately, because when tightening, the functions of the hands will be partially lost. In rare cases, fixation with knitting needles is used.
An internal fracture with fragments and displacement is treated with bone grafting. Additionally, fixing plates are installed. Due to them, a complete, but meanwhile natural fixation of the hand in one position is achieved. This contributes to the rapid fusion of bones.
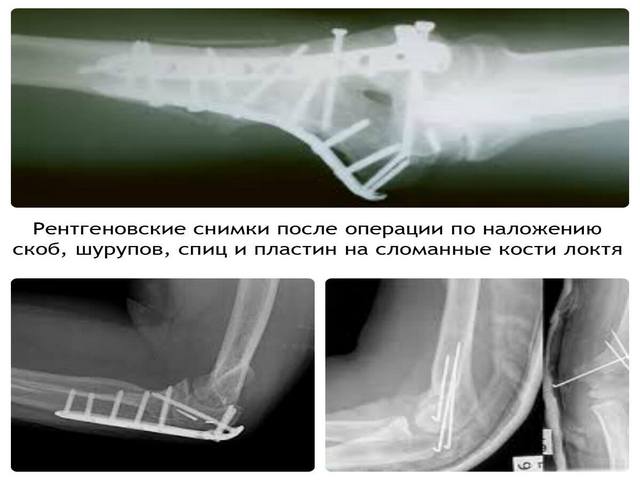
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation actions begin during the treatment period - after 14 days it is recommended to strain the muscles of the arm under the cast. After that, physiotherapy is prescribed, which consists in magnetotherapy. The impact is made directly through the plaster cast.
Recommendations on how to develop the elbow joint can only be given by a traumatologist. After the bandage is removed, additional physiotherapeutic actions are connected - electrophoresis, mud baths and sea salt baths. The hand after the fracture must be massaged.
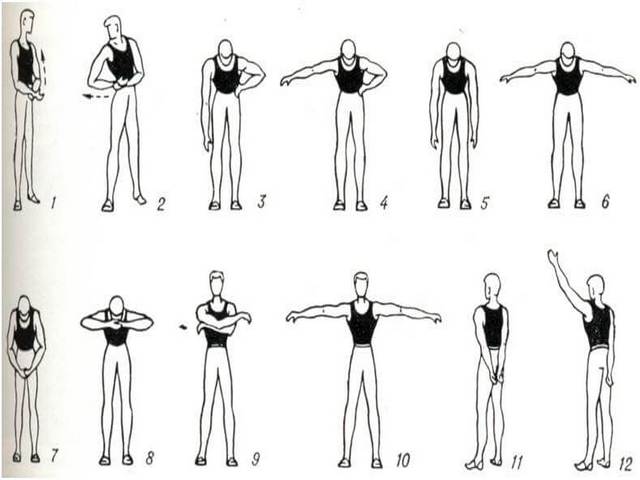
The elbow joint after a fracture needs a serious and purposeful development for the full restoration of all functions. Approaches to exercises are performed in 10 repetitions, the number of which increases gradually. They must be performed three times a day.

In addition, it is recommended to diversify daily meals with foods that contain magnesium and calcium. This will contribute to the restoration and fusion of bones. With preventive actions, you need to take vitamins aimed at resuming the missing substances in the body.
It is possible to recover from a fracture of the elbow joint, but it will take enough time. That is why such injuries can be characterized by both rapid healing and slow development. motor function. Any injury, including a fracture of the elbow joint, can also provoke a considerable number of chronic diseases in the future. The fracture of the arm at the elbow is not yet a sentence, so you should not give up. Timely implementation of medical recommendations will contribute to rapid healing, and mobility in the arm will return after exercise.
22
Jun
2014
The elbow joint is complex mechanism, formed by the radius, ulna and humerus, and contains in its structure many vessels and nerves. With the help of this joint, the human hand has greater mobility and allows you to perform quite different movements in amplitude. Injuries to this joint, including a fracture, are a common occurrence that requires serious treatment, including surgical intervention, sometimes even repeated. An elbow fracture is the destruction of one or more bones or processes that enter the elbow joint.
Types of fractures of the elbow joint
All fractures of the elbow joint can be divided into categories.
- Intra-articular fractures - there is a rupture of the tendon of the triceps muscle, and the bone fragments are displaced upward
- Periarticular fractures - tendon rupture and displacement are not observed and
- Closed fractures - without violating the integrity of soft tissues and skin.
- Open fractures - the integrity of the skin is violated.
- Comminuted fractures - separation from the end of the bone of one or two fragments
- Shattered fractures - there are a large number of small fragments.
- Incomplete fracture - a crack in the bone is formed.
- Along the fracture line, transverse, longitudinal and oblique fractures can be distinguished.
- Often, a fracture is combined with a dislocation and is called a fracture-dislocation.
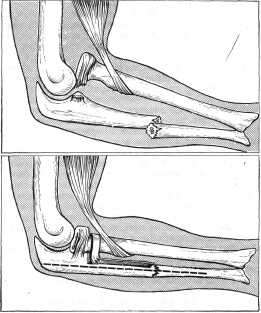
The most common of the above types of fracture is intra-articular - a fracture of the olecranon, which does not have muscle protection. It occurs when a person falls from a height of his height, when a person instinctively puts his hand under him. However, the process itself rarely breaks, more often fragments come off from it, which often injure blood vessels, nerves and ligaments.
Signs and first aid for a fracture of the elbow joint
With a fracture of the elbow, the following symptoms are noted.
- Sharp pain in the elbow, radiating to the forearm, wrist and fingers.
- Edema, swelling and hematoma at the fracture site.
- Inability to move or severely limited mobility.
- With an open fracture, bleeding and exposure of the bones.
- Atypical lateral mobility of the forearm, not characteristic of healthy mobility.
- In some cases, when the nerve fibers are affected, there is numbness and tingling in the forearm area.
- Inability to hold one's own hand, but only supporting it with the other hand.
- Creaking or clicking sound when moving the hand.
- Elbow joint deformity.
- Cold, pale bluish skin in the area of the affected area.
If any of the above symptoms are present, emergency medical attention is needed.
How to help the victim before the doctor arrives
- Transport immobilization - fixation of the limb in the most immobile position for transportation to the emergency room.
- An open wound, if any, should be covered with a clean bandage or cloth.
- When bleeding, you need to raise your hand as high as possible.
- Apply a cold compress or ice to the injured area to relieve swelling.
- In no case should you try to set a broken bone yourself, especially with an open fracture.
Diagnostic methods
 Before the examination, the doctor must ask you important questions about the state of health of the patient in order to identify chronic diseases, previously suffered injuries and intolerance to certain substances or preparations, the method of obtaining this injury and the circumstances accompanying it. This is done in order to have a complete picture of the situation and make the most reliable diagnosis.
Before the examination, the doctor must ask you important questions about the state of health of the patient in order to identify chronic diseases, previously suffered injuries and intolerance to certain substances or preparations, the method of obtaining this injury and the circumstances accompanying it. This is done in order to have a complete picture of the situation and make the most reliable diagnosis.
To diagnose an elbow fracture, a doctor must take x-rays. In the main X-ray is made at two angles. If the pain is completely unbearable, then an x-ray can be performed under light anesthesia. In some cases, x-rays of both limbs are taken, for example, in children, because in early age unformed cartilage can be mistaken for a fracture. This requires a comparison of a healthy and injured hand.
It is possible to refer the victim to an ultrasound examination, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
If an artery ruptures, a doctor may prescribe an arteriogram. This procedure consists in introducing into the arterial blood contrast agent so that it can be determined in what place and how badly the artery is damaged, so that later it can be quickly restored.
Treatment Methods
An elbow fracture is a serious injury and, of course, requires treatment. The choice of treatment method depends on the severity of the injury. In any case, after damage to the elbow joint and first aid to the victim, a qualified specialist puts accurate diagnosis after a thorough examination. Based on it, the treatment is chosen.
Specialists distinguish two main large categories of fractures - a simple fracture and a fracture with a displacement.
With a simple fracture, without fragments and displacement, a plaster is applied to a large area of the arm - from the humerus to the fingers. The arm is fixed bent at the elbow joint. A plaster splint is worn by patients for 4 weeks, then another one with periodic removal to start developing the joint.
With a periarticular fracture, conservative treatment, all traditional procedures and rehabilitation measures are indicated.
With a fracture with a displacement, comminuted, fragmented, the treatment will be more serious and lengthy. The clinician will need to assemble the entire joint into its anatomical starting position by means of surgical operation. In some cases, the bones are held together with special devices - screws, bolts and wires, which are removed after a few months. After surgery, the arm is fixed at an angle of 30-60 degrees. This is done to improve blood flow, reduce swelling and hematoma. A cast is applied for 5-6 weeks, depending on the severity of the fracture. In addition to everything, drug treatment is carried out with drugs aimed at relieving inflammation, swelling, general strengthening and maintaining the body in the postoperative period.
Rehabilitation activities
IMPORTANT!!! To avoid injuries to the limbs, it is necessary to follow the elementary rules of life safety, and if an injury does occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. The elbow joint is a multifunctional complex mechanism that has a complex structure and includes a large number of components. Only a doctor can prescribe competent treatment and eliminate the risks of complications and irreversible consequences. Self-medication is dangerous to your health.
It is better to start the recovery period after a fracture of the elbow 2-3 days after the application of a plaster splint or surgery. On the second or third day, you can move your fingers as far as the condition allows. After 8-9 days, you can try to unclench and squeeze the muscles under the cast, as in a fixed position, the ligaments and tendons can atrophy. After 2 weeks, the doctor may prescribe magnetic therapy, and after removing the cast, other physiotherapy procedures aimed at restoring the functions of the elbow joint. These are electrophoresis, UHF, mud therapy, baths with sea salt.
An integral part of the rehabilitation period is physiotherapy, which includes a specially designed set of exercises. Here are some of them.
- The hands must be closed into a lock and gradually thrown over the left, then the right ear, while stretching the muscles.
- Closing hands on the back.
- Ball game.
- Rolling a children's toy car on the table back and forth. When performing this exercise, the elbow joint makes many movements that restore its mobility well.
- Exercises with dumbbells weighing no more than 2 kg can be used after the pain syndrome has decreased, since with still existing edema and residual inflammation, an extra load on the joint is contraindicated.
- Gradual development of rotational movements in the forearm.
You should not make sudden movements, in vain thinking that having endured pain, you can achieve quick results. All exercises require slow and smooth execution, with a gradual increase in the number of repetitions and intensity.
