Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine are observed in 80% of the adult population of the planet. They worsen the quality of life and lead to development serious complications. How to avoid pathologies?
Take any person: everyone has suffered from lower back pain at least once in their life. Medical statistics say: 20% constantly complain of lumbar pain, and 1-3% require surgical treatment.
The lumbosacral region is the center of gravity of the body; it takes on all the loads accompanying any movement of the human body. Sometimes these loads exceed permissible limits, temporary changes and deformation of cartilage tissue occur in the spine. Under the influence of pressure on the damaged area of the spine, salts present in the bloodstream and plasma begin to actively penetrate into its structure. Calcification of a certain area of cartilage tissue begins. These are degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine.
How do degenerative changes in the lumbar spine develop?
For degenerative changes to move into an irreversible phase, a lot of time must pass. And this time the disease plays out in a person, due to the fact that the disease does not manifest itself immediately.
Pronounced symptoms show themselves when time is lost, and the degenerative changes themselves have become large-scale and irreversible.
The medical term “degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine” summarizes several diseases:
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbar spine: main symptoms
The clinical picture of changes may vary, depending on which spinal structures are damaged and how serious the damage is.
Symptoms of diseases appear as degenerative-dystrophic lesions develop, but at initial stages pass without pronounced external signs.
As the pathological process develops, the patient may feel stiffness and heaviness in the lower back. But the main symptom of all degenerative changes spine - pain. Pain in the lumbar region occurs during long walking and physical activity, prolonged sitting in one position, and bending. The pain syndrome is wave-like: it arises, then decreases, and disappears.
The progressive degenerative process in the intervertebral discs of the spine can lead to serious and dangerous complications.
Degenerative changes develop in stages:
Initial stage
The first symptom that “screams” about the presence of pathological changes in the lumbar spine is a pronounced pain syndrome in the lower back. The pain is so noticeable that the patient is forced to limit his movements, and this significantly reduces normal level life and performance.
Complaints of pain directly depend on the location of the lesion.
Second stage of the disease
Further progression of degenerative changes is characterized by the presence of:
- severe mobility limitations;
- “lumbago” that occurs in the lower back;
- tingling and goosebumps in the limbs and buttocks.
At the second stage of the disease, radicular syndrome develops - compression of the nerve roots occurs.
Third stage
At the third stage, blood circulation is disrupted due to compression of the radicular vessel, which leads to the development of ischemia. In addition to increasing pain, the third stage is noted:
- partial or temporary numbness in the lower extremities;
- convulsions.
Fourth stage
Degenerative pathological processes of the spine that have not received proper treatment at the fourth stage of development are fraught with paralysis and paresis. These complications arise due to complete disruption of blood circulation spinal cord.
Causes of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine
The human body is a delicate and calibrated mechanism. It is determined by nature itself that the load on the human spine should be distributed evenly. A healthy spinal column can withstand both jumping and heavy lifting. But all this works only when a person watches his posture and has a strong muscle corset. The modern lifestyle is sedentary. And this leads to weakening of the muscle corset and weight gain.
Sedentary work contributes to the appearance of degenerative changes in the spine.
According to research, the human spine is in a bent position 75-80% of the time: the intervertebral discs become less elastic, and the vertebrae become deformed.
Due to degenerative changes, intervertebral discs lose moisture, cracks and all kinds of ruptures form in them. This contributes to the appearance of intervertebral hernias. When the load changes, the vertebrae try to increase their area, grow, and become increasingly thick, pinching the adjacent nerves.
Reasons that provoke pathological changes:
- constant or sudden loads;
- active sports with heavy loads;
- injuries;
- natural aging;
- inflammatory diseases of the spine;
- poor nutrition.
Treatment methods
Degenerative-dystrophic changes lumbar region spine, unfortunately, are observed in a large number of people, and therefore the question of how to treat these pathologies is very relevant.
After all, if degenerative changes are not treated, they will progress, and the consequences can be very dire, including disability due to impaired motor activity.
Treatment of diseases of the lumbar region is considered complete and promotes recovery if after treatment the following is observed:
- reduction or disappearance of pain;
- relieving muscle tension in the lumbar region, pelvis and lower extremities, strengthening muscles;
- improvement of blood flow and supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen, normalization of metabolic processes;
- removal or reduction of inflammation;
- normalization of lumbar sensitivity;
To achieve the above results it is necessary correct treatment. Experts prescribe complex therapy using the latest advances modern medicine. For the treatment of degenerative changes in the lumbar sacral region spine is prescribed:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- massage, therapeutic exercises, manual therapy;
- acupuncture, acupuncture;
- in extremely severe cases - surgical intervention.
Conclusion
From all of the above, it follows that diseases of the lumbosacral region can be overcome in several ways. But it is better not to allow irreversible pathological processes to occur. You should consult a doctor on time, monitor your health, and lead a correct lifestyle.
Today the most common are. Sedentary work, a sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, excessive physical activity - all this leads to the appearance of degenerative changes in the lumbosacral spine. It is necessary to consider in more detail what this is.
Possible complications
This condition is observed in pathology intervertebral disc, which is accompanied by lower back pain. The intervertebral disc does not have blood vessels, therefore, is not supplied with blood. For this reason, it cannot repair itself in the same way as other body tissues. Despite the seriousness of this condition, it occurs in 30% of people over the age of 30. Although earlier cases cannot be ruled out. Such damage to the spine is not always accompanied by pain. After 60 years, dystrophic changes are already a pattern.
If this condition is not treated in time, it will lead to complications. Due to pinching of the intervertebral canals, nerves are damaged. Then the nerve endings swell, their conductivity decreases (therefore, numbness of the limbs and a feeling of fatigue in the back occur). The vertebrae change their growth pattern: to reduce the load, they expand. This leads to osteochondrosis and more pinched nerves. If an infection (bacteria, fungi) is added to this process, then diseases such as arthrosis, arthritis, and osteochondropathy develop. Degenerative changes in muscles lead to scoliosis, displacement of the vertebrae. Severe conditions are accompanied by ischemia, circulatory disorders, paresis, and paralysis of the limbs. A person may become disabled.
Causes of the disease
There are several reasons for the appearance of this syndrome:
- Sedentary lifestyle. In a healthy body, the load on the spine is distributed evenly. But due to a sedentary lifestyle, the muscle corset weakens. The muscles do not provide reliable support for the spine, as a result of which even a small load can be fraught with displacement and destruction of the vertebrae.
- Active sports. Not only the lack of load can lead to the appearance of degenerative changes in the lumbar spine. Excessive exercise also has a negative impact on health. Many athletes have joint problems.
- Injuries. IN at a young age the presence of diseases such as arthrosis, pinched nerve, intervertebral hernia is usually associated with injury. This includes birth injuries.
- Degenerative changes are often associated with the aging process of the body. In this case, the changes are irreversible. And treatment does not imply drastic measures (surgery): only supportive therapy is carried out.
- Poor nutrition. Due to impaired metabolism, the body's cells do not receive sufficient nutrition. Limiting certain foods affects the condition of the entire body. Abuse junk food leads to obesity. This creates additional stress on the spine.
- Inflammatory diseases of the spine. For example, arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis.
- Hypothermia.
The causes of pain are 2 factors:
- When a hernia forms between the vertebrae, the proteins in the interdisc space begin to irritate the nerve endings. This causes inflammation.
- Excessive mobility of the vertebrae in the affected area.
Signs of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine
The following symptoms of the syndrome are known:
- The main symptom is pain in the lower back. It can radiate to the legs and buttocks (sciatica). Lower back pain is usually aching and dull.
- Numbness or tingling in the lower extremities.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs (impaired urination, defecation), violation reproductive function, weakness in legs.
- Feeling of stiffness in movements. This is especially felt in the morning when getting out of bed. The patient needs to “diverge” in order to fully move.
- Local increase in temperature. The area where degenerative changes are observed becomes hot.
- Redness, swelling.
- Asymmetry of the buttocks.
Typically, spinal diseases are chronic, characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission.
During an exacerbation, the symptoms become very pronounced, especially pain. During remission, a person may feel practically healthy.
Types of diagnostics
- X-ray;
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
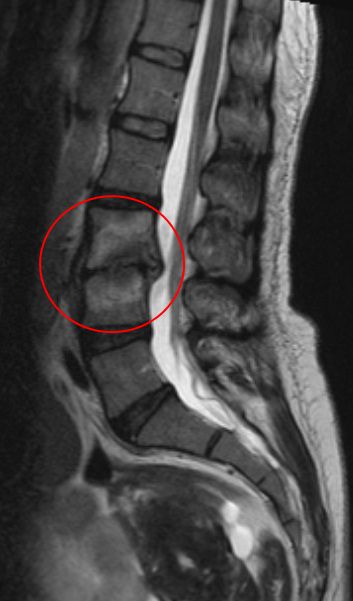
The first of these methods is the most accessible, but at the same time the least informative. X-rays provide information about the location of the bones and deformities of the spine. It is able to detect the disease in its later stages. CT and MRI - more modern methods. MRI allows you to see the destruction of the disc space, disc dehydration, erosion of the cartilaginous end plate of the vertebral body, the presence intervertebral hernia, rupture in the annulus fibrosus. But such procedures are usually expensive.
As a reward for the ability to walk upright, the person additionally received various problems with the spine. The emergence of pathologies is also facilitated by modern world, which minimized any movement. Nowadays it is easier for a person to drive one stop than to spend a little more time walking.
Pathogenesis and causes of degenerative changes in the lower back
People are accustomed to associate all pain in the lumbar region exclusively with lifting something heavy. That is why people with lumbodynia in the first stage rarely go to the doctor and try to cure the symptoms at home (rubbing in ointments, painkillers, etc.), and not the cause of the inflammatory reaction. Scientists have conducted research and discovered a number of factors influencing the occurrence of degenerative changes:
- Age. After 30 years, the body stops providing enough nutrients for the regeneration of bone, joint and cartilage tissues, so the destroyed segments cannot recover on their own.
- Genetics. If there were problems with the musculoskeletal system in the family, then many disorders in the spine develop faster than in healthy person no risk factor. Preventive measures (physical therapy, nutrition control, balanced sleep and rest, orthopedic mattress, etc.) help eliminate or slow down a genetic predisposition.
- Old injuries. Subluxations, microfractures and minor displacements of the vertebrae due to an impact do not always manifest themselves as painful symptoms and the person continues to live a normal life. But such changes affect the redistribution of the load across the back, which leads to excess pressure on the lower back. This applies to people who do not change their body position for a long time (sitting or standing work). Under such conditions, the vertebrae experience severe compression, which disrupts the functions of the cartilaginous segments of the spine.
- Lifting a large weight, without additional support for the lower back (bandage or belt), leads to microtrauma of discs and cartilage tissue, disruption of trophism, nutrition, regeneration, etc.
The causes of pathologies in the lower back are often poor nutrition, bad habits, overweight, pregnancy, menopause in women, poor environment, improper bedding, contaminated water, etc.
The mechanism of development of changes is associated with heavy loads on the lower back. The lumbar region feels even a person’s own weight twice as strongly, and any load only increases the compression between the vertebrae. Degenerative dystrophic changes in the lumbar spine are associated with the following processes:
- Malfunctions in the nutrition of the discs and their structural fragments, which leads to gradual degeneration.
- Destruction and compression of the fibrous ring affects the height between the discs and leads to destruction of the fibrous membrane. This is how pathological protrusions appear, which later develop into protrusion. An imbalance in the proportional distance between the discs can lead to pinching of the nerve processes.
- Pinching produces an inflammatory reaction, leading to degenerative changes in cartilage and joint tissue. During inflammation, prostaglandins are released as a response immune system. This leads to swelling of the tissue in the pinched area and the appearance of pain symptoms.
The pathological reaction can take a long time, and specific symptoms do not always appear in the first stages of the disease. In most patients, the onset of inflammation is latent.
Signs and diagnostic methods for studying degenerative changes in the lower back
Among the symptoms of this pathology, lumbodynia occupies a special place. This term describes exactly lumbar pain, which cannot be confused with pain in other parts of the spine. In this case, the pain is aching in nature, and lumbago (lumbago) in the lumbar region is rarely noticed. Possible radiation to the buttocks and legs. Other signs include:
- Unpleasant sensations in the pathological area (tingling, burning, numbness, etc.).
- Failures in thermoregulation of the lumbar region.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the pelvic organs.
- Limitation of range of motion. Clearly manifests itself when bending and turning.
- Stiffness of movement, often occurs in the morning.
- Body asymmetry, which is clearly visible on the buttocks.
- Swelling of the affected area.
- Redness at the site of discomfort.
Symptoms are clearly manifested during the period of exacerbation and are poorly noticeable during the period of remission. To determine the location of the change and staging accurate diagnosis use various methods diagnostics:
- X-ray. It is the most accessible research method, but is prohibited for repeated use. Such diagnostics can give an almost complete picture of the condition bone tissue, but does not allow you to find pathologies of soft tissues, joints, ligaments, etc.
- Computed tomography. The method is based on the use of X-rays, but provides a more detailed picture of the condition of the spine in several projections.
- MRI. Now this is the safest and most accurate method for diagnosing spinal diseases. Magnetic waves penetrate into soft fabrics, so the doctor gets a complete picture of the condition of each segment of the spine.
Treatment of degenerative changes in the lumbar region
Having studied all the collected data on the disease, the doctor selects the optimal conservative treatment, which includes:
- Relief of pain syndrome. Dosage forms containing anti-inflammatory and analgesic substances are prescribed. These groups include analgesics and NSAIDs, which are used in the form of injections, ointments, tablets, gels, emulsions, etc. For emergency relief of an acute attack, you can apply a cold compress.
- Relieving muscle spasms. For this purpose, muscle relaxants are prescribed, the effect of which is to relax the muscle corset. They are used for a limited time, since regular exposure reduces muscle tone.
- Restorative drugs during remission. These include chondroprotectors that restore cartilage and joint tissue, and complexes of vitamins and minerals necessary to nourish bone tissue.
- Massage and physiotherapy. They help restore blood circulation, normalize metabolic processes, stimulate the body to self-heal, etc. Some physiotherapy procedures allow you to deliver medicinal components directly to the location of the pathology.
- Manual therapy. Aimed at stimulating the body to self-healing. To do this, the specialist acts on certain points of the body.
- Exercise therapy. Is the main component conservative treatment, as it helps restore the elasticity of the muscle corset, restores correct posture, stretches the spine, strengthens connecting fragments, etc. All exercises must be performed regularly, avoiding sudden and jerky movements.
- Diet. The patient needs to balance his diet by adding jelly-like foods, B vitamins, calcium, fluoride, etc. For overweight people, it is recommended to consult a nutritionist who will select the right diet.
- Hirudotherapy, paraffin therapy, acupuncture. Such techniques affect overall well-being, improve metabolic processes and trigger a self-healing mechanism.
Over 80% of people over 55 years of age suffer from abnormalities spinal column. Of these, the most common are degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbosacral region with to varying degrees complications.
It is worth noting that until recently, damage to cartilage tissue was considered a disease of senility. But every year the age threshold decreases. Even at 30 years of age, there is a possibility of developing trophic changes in the lumbar spine - about 30% of clinical cases.
Recent medical studies have refuted the information that dystrophic changes in the lumbar region are natural processes and occur due to aging. According to the latest information, external factors and chronic diseases may also be causes of deviations. Scientists have well studied the mechanisms leading to disruption of the trophism of cartilage tissue. Therefore, there are a lot of treatment methods.
Why does the disease develop?
It is possible to understand what degenerative changes in the lumbosacral spine are only by studying the basic prerequisites for the development of this anomaly. It should also be understood that human body - complex mechanism, capable of withstanding different, even the highest loads. However, negative impact external factors weakens natural defense systems, which is why cartilage tissue loses its strength.
The condition of the spine depends especially strongly on lifestyle. Therefore, a number of triggers are identified that contribute to the development of degenerative and dystrophic anomalies:
- old, untreated spinal column injuries;
- natural aging of the body;
- inflammatory processes;
- problems with the endocrine system;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- intense physical activity;
- sudden loads on the ridge;
- unhealthy diet;
- hypothermia of the body;
- changes hormonal levels.
Anatomically, the spine is designed to accept and evenly distribute the load. The supporting muscular frame also helps him in this. Therefore, a sedentary lifestyle leads to various deviations in the development of the ridge.
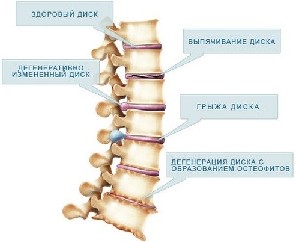
Such people usually experience problems with excess weight. Their muscles are poorly developed and any load instantly overloads the intervertebral discs. Since the muscular frame is not able to take part of the load on itself, degenerative dystrophic changes in the lumbar spine develop very quickly.
There are a huge number of other factors that adversely affect the development of the ridge. Moreover, often the spinal column is affected by several triggers at once. Therefore, it is almost impossible to independently determine the source of the problem. On the other hand, using medical care, you can not only find out the cause of the disease, but also prevent the progression of degenerative disorders.
How the disease develops
The spinal column has to deal with large amounts of stress every day. Regardless of whether any movements are performed or a person sits motionless, the spine is influenced by certain forces. And the heaviest load falls on the lumbar region.
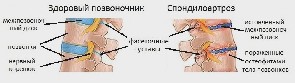
It is under the influence of external factors that abnormal changes begin to form intervertebral discs. The cartilage tissues are the first to be affected. Moreover, pathogenesis occurs in stages:
Characteristic symptoms
In the early stages, pathology is quite difficult to determine. Degenerative-dystrophic processes are not accompanied by pain or discomfort and can be very asymptomatic for a long time. Naturally, signs of damage to cartilage tissue appear gradually, with the progress of negative changes:
- There are no obvious triggers. Only a specialist can determine the onset of the disease. Rarely, after physical activity, appear dull pain in the lumbar region. Some limited movement is possible.
- The severity of symptoms increases. The mechanics of the entire body are seriously impaired. The slightest bending is accompanied by sharp pain, described as “lumbago.” “Goosebumps”, numbness and tingling of the lower extremities and buttocks appear. All this may indicate the onset of radiculitis.
- The pain syndrome intensifies and comes acute stage diseases. Limbs are increasingly becoming numb. The nutrition of the soft tissues of the ridge is disrupted, and compression of the radicular vessels occurs.
- With the appearance of the first signs of degenerative changes in the spinal column, the chances of damage to the radicular nerves and the spinal cord as a whole increase. Partial paralysis is possible.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
Due to the absence of symptoms on early stages, independent identification of the problem is difficult. Often a person learns about degenerative-dystrophic changes after a routine medical examination. If a visit to the doctor is caused by unexpected pain in the lumbar region, most likely the disease has begun to progress.
It is very important to identify the problem before the first complications appear. Therefore, modern clinics use different diagnostic methods to cover the entire range of possible irritants.
Modern diagnostics
It all starts with an external examination. The doctor listens to the patient's complaints, examines the back, and palpates the spine. This helps to make a preliminary history and make some assumptions.
![]()
But an external examination cannot boast of accuracy, even if the specialist is very experienced. Therefore, it is complemented by other procedures aimed at assessing probable pathologies of the intervertebral discs.
A comprehensive examination includes:
- general blood test;
- lumbar x-ray;
- computer tomography;
It is important to remember that simple x-rays may not be sufficient. This is a very common, but outdated and inaccurate diagnostic method.
CT and MRI make it possible to more accurately and in detail visualize the current condition of the spine and identify degenerative changes in the early stages. Moreover, the coverage of the examined area is much greater: it is possible to detect problem areas in the thoracic region.
Effective treatment
To prevent the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes, it is necessary to undergo a course of drug treatment:
- Doctors often prescribe ointments and creams with analgesics, injection blockers and other means aimed at quick withdrawal pain syndrome.
- Also used medicines, helping to improve blood flow around the spinal column. Taking these medications is necessary if there is swelling of the soft tissues. In addition, such drugs prevent spasms and improve the trophism of cartilage tissue.
- If there is compression of the radicular nerves, it is important to provide the body a large number vitamins The B-group is especially valued. Useful microelements increase the speed of recovery of nerve fibers.
The list of drugs can be very different. In many ways, the choice of a particular medication is influenced by the general picture of the disease, the condition of the spine and the patient’s sensitivity to the active components.
Disease prevention
It is important to understand that one drug therapy not enough. Treatment of symptoms only stops negative trophism, relieves pain and nourishes soft tissues. It is necessary to consolidate the results of treatment to prevent relapses. 
For prevention the following is prescribed:
- physical therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- diet.
Particular attention is paid exercise therapy complex. Regular execution Correctly prescribed exercises will help strengthen the muscle frame and align the spinal column. In this way, it will be possible to avoid degenerative lesions in the future.
Negative changes in the spine are not a separate disease, but a whole complex individual problems. However, disorders of the lumbar and other regions are treatable. The main thing is to be patient and follow all medical instructions.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbosacral spine are pathological syndrome in the area of the intervertebral disc, causing pain in the lumbar area.
In addition to functional disorders in the functioning of the lumbosacral region, there are degenerative-dystrophic changes with the threat of formation intervertebral hernia and in other parts of the spine. Signs and symptoms, as well as treatment methods for pathological dysfunctions will be discussed in this article.
Lower back pain: causes, symptoms and treatment
It is generally accepted that degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine are largely associated with genetic predisposition. However, hereditary causative factor pathological condition has a small percentage of the total neurological diseases. It should be taken into account that the result of degenerative changes in the spinal column may be the natural aging of the body, traumatic conditions and other components. Also a common cause of pathological deviation is the result of chronic diseases associated with the functional functioning of the skeletal and joint system:
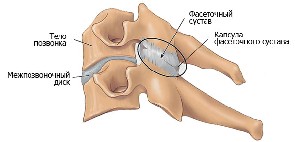
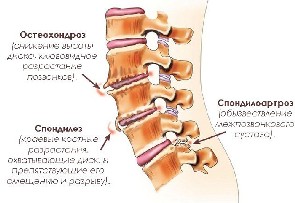
· spondyloarthrosis – arthrosis of the intervertebral joints;
· osteochondrosis – the process of thinning and wear of the intervertebral discs of the sacrolumbar region;
· spondylosis – formation of bone growths along the edges of the vertebrae.

However, most often degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbosacral region can be caused by an intervertebral hernia, which forms in the annular connective tissue plate, forming the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc. The process of formation of an intervertebral hernia occurs as follows. The nucleus pulposus, which is a semi-liquid structure of fibrous tissue and a gelatinous substance - chondrin, as a result of displacement, extends beyond the fibrous ring. This condition in the peridiscal space begins to put pressure on the nerve roots, causing irritation of the nerve endings, as a result of which the person experiences pain and discomfort. Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbar spine can be determined by the following symptomatic signs:
localized acute or It's a dull pain in the lower back, with characteristic radiation to the hip and lower limb;
· tingling or numbness in the legs, often causing lameness;
· stiffness in movements (turning the back, bending).
Magnetic resonance imaging will help to definitively establish the type of degenerative transformations in the lumbosacral region. Based on the results of scanning and identification pain syndromes the appropriate type of medication is selected.

Conservative treatment methods can effectively combat the disease. Massage, physiotherapy and physical therapy- these are ideal forms of influence on a neurological problem. Naturally, during exacerbation of the disease, certain pharmacological drug combinations are used, mainly non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs.
Symptoms, signs and treatment of the cervical spine
Degenerative-dystrophic changes cervical spine spine may be manifested by the following symptoms:
· discomfort in the back and neck area;
· muscular neck pain, extending to the occipital zone of the cervical vertebra;
dizziness and/or headache;
· decreased visual acuity;
Numbness and/or tingling upper limbs;
· pressure in the temporal zone;
· constant ringing in the ears.

All these signs indicate a chronic condition of the cervical spine and require careful diagnostic examination followed by preventive treatment. The cause of intervertebral inflammation can be:
· overload of the spinal motion segment;
· micro-tears and/or microcracks in intervertebral discs;
· muscle strain;
· formation of intervertebral hernia in the cervical spine;
· reducing the distance between the vertebrae due to compression.
Medical care for cervical osteochondrosis begins with identifying symptomatic signs, the main indicator of which is the fingers. If degenerative processes occur in the segmental zone between the seventh cervical and first thoracic vertebrae, then the person complains of numbness in the little finger and/or ring finger. Discomfort in the index and/or middle finger indicates degenerative problems between the sixth and seventh. cervical vertebra. A more accurate confirmation of the preliminary diagnosis is established using an X-ray scan of the cervical spine. Effective method treatment cervical osteochondrosis is manual therapy and application dosage forms to improve metabolic process in the problem area.
In most cases, degenerative-dystrophic changes thoracic spine are associated with physical inactivity, that is, a lack of load on muscle structures, which, in turn, weakens the muscular corset of the thoracic region and increases pressure on the articular ligaments and discs of the spine, thereby causing thoracic osteochondrosis. Other cause-and-effect factors in the development of the disease include:
- difficult conditions professional activity person;
- congenital defects of the bone frame of the spinal column;
- infectious lesions and chronic diseases of the bone and/or joint system;
- changes in hormonal levels due to age-related changes in the body;
- hypothermia;
- violation of metabolic processes.
Clear symptomatic signs of thoracic osteochondrosis are:
- pain in the interscapular area, spreading to the thoracic region;
- intercostal neuralgia, when compression of nerve endings occurs;
- strong pain sensitivity in the affected area.
In addition to these symptoms, when visiting a specialist, patients complain of problems with organs gastrointestinal tract, respiratory and genitourinary system. Unpleasant pain in the chest area often resembles symptoms of angina pectoris, which is why the diagnostic process is somewhat delayed. However, after a confirmed diagnosis, you can confidently begin treatment and preventive measures. Surgical intervention for thoracic osteochondrosis it is practically not used, the only condition is a threat to the functional functioning of the internal organs.
Almost all methods of treating problem areas of the spinal column are treated in the same way. The active use of various chondroprotectors, muscle relaxants, anti-inflammatory, non-steroidal and vasodilating drugs is the basis of conservative treatment. After removal pain Rehabilitation of the thoracic spine is carried out using massage, special gymnastic exercises, and phytotherapeutic procedures.
A healthy lifestyle is an excellent prevention of any diseases of the spinal system.
