The temporomandibular joint is a complex structure, despite the small range of movements performed. It consists of two separate joints, isolated from each other by a septum consisting of bone and connective tissue. Four paired muscles ensure the sole purpose of the joint - chewing. Violation of this function immediately worsens a person’s quality of life, forcing him to seek treatment from a doctor.
Only a qualified dentist can help you determine the cause of your jaw pain. ![]()
The temporomandibular joint is the connection between the lower jaw and the temporal bones of the skull. Your dentist can help you do accurate diagnosis. Jaw is blocked, blocks or leaves the site Sensitivity of the jaw muscles Inflammation of the face.
- Pain in the face, jaw or ear.
- Headaches, ear pain, pain and pressure in the back of the eyes.
- A clicking or clicking sound when opening or closing the mouth.
Symptoms
The manifestation of any pathology will be dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, which combines a number of different symptoms. They will have different characteristics depending on the cause, but pain is a consistent sign of injury. It can take on different shades or severity, sometimes leading the doctor away from the correct diagnosis. But a number of special tests and characteristic symptoms(with adequate examination), they will not allow you to miss the real reason pain.
Medicines - try to eliminate muscle spasms and pain by applying moist heat or medications such as muscle relaxants, aspirin or other over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs. Wear a night mouth protector - Reduce the painful effects of teeth grinding or clenching by using a night mouth finger or plate. Relax - Learn relaxation techniques to help control muscle tension in the jaw. Your dentist can help you or give you advice to help you eliminate stress. Temporal joint dysfunction is a complex and multifactorial condition that is not fully understood.
The severity of symptoms depends entirely on the cause of the dysfunction, so in some cases the patient may go straight to the hospital, suspecting acute inflammation.
Joint dysfunction can vary in nature - from acute and unbearable symptoms to mild discomfort when chewing. Therefore, the main task of identifying such patients lies with dentists - it is to him that patients often turn for preventive purposes. And during the appointment, a problem is inadvertently discovered—impaired mouth opening when the doctor tries to carry out manipulations. The disease is characterized by a standard set of signs that give a complete picture upon examination:
Although many forms of treatment have been tested, none have produced entirely conclusive results. Outcomes were extracted a priori and in a standardized manner, evaluating acupuncture compared with sham acupuncture, conventional therapy, or no treatment. Randomization details were insufficient to determine whether the appropriate method was used and whether the site was effective at the time of study entry. All studies used both local and distant points, and dysfunction indices were reported in all cases.
- Pain is the main indicator - it is rarely detected at rest. To provoke it, it is enough to clench your teeth tightly.
- Limitation of mobility is rarely detected by the patient himself, as it develops gradually. Moreover, there is a difference between inflammatory and traumatic origin. Damage leads to the simultaneous development of pain and dysfunction, and with inflammation, various combinations of these are observed.
- The last common symptom is a change in the appearance of the facial area. This primarily concerns the cheeks, which are shaped by the branches. lower jaw And masticatory muscles. With pathology of the temporomandibular joint, they are actively involved in the destructive process, which immediately changes appearance faces.
At acute course diseases, people immediately seek treatment - the prognosis is worse in indolent forms of the disease, when persistent changes have time to form in the joint.
The study did not have a blinded group, and clinical presentation of the dysfunction index was not shown to mask the patient's site site. In the third study, information on attrition was not available. None of the studies reported adverse effects on treatment. In all studies, acupuncture was applied to regions corresponding to the patient's symptoms, using local and distant points.
The needles were manually stimulated, but in 1 study there was 2 Hz stimulation in 2 needles of the third treatment, which resulted in muscle contraction. Raustia et al compared acupuncture with standard dental treatment without including a combination of counseling, occlusal adjustment, muscle exercises and occlusive plaque. The average age was 8 years in group 1 and 26.4 in group 2; 78% are women. Both treatments had similar results in the dysfunction index: dental treatment was significantly better after one week of treatment, but not after 3 months.
After the diagnosis is established, the question of choosing a treatment method is immediately decided - whether it is possible to do without surgery. Most patients are treated with conservative methods that create temporary rest in the joint. But here, too, everything depends on the cause of the pathology - in advanced cases, the changes become so pronounced that it is simply impossible to do without surgery.
There was also a significant difference between the effects on mouth opening, with acupuncture providing higher values with a lower initial value, while traditional treatment was higher in the initial values. There was no difference in subjective pain rated by patients between the two experiments. The same researchers presented a dysfunction index for patients individually, emphasizing the components of the index for high- and low-scoring subgroups. There was no difference between the two treatments for any of the components.
Rheumatoid arthritis
With this disease, damage to the joints occurs, caused by a disruption in the functioning of one’s own immunity. As a result, antibodies are formed to the joint tissues, which lead to continuous destruction of cartilage and synovial capsule. Dysfunction of the jaw joints against the background of this disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
Johansson and colleagues compared acupuncture with 3 to 7 local points and a distal point with full maxillary acrylic resin occlusal plate coverage versus an untreated control group. Patients who had previous experience with acupuncture or occlusive bites were excluded.
The average duration of pain was 4 years. The occlusal plates were rigid, fully covered acrylic fixtures designed to fit the jaw. Only 3 patients with loss of molar support in the mandible had a plaque applied to the mandible instead upper jaw. A battery of 7 outcomes was used: medical history, subjective assessment, activities of daily living, visual analogous pain scale, pain frequency, medication use, and clinical dysfunction index. Results were reported for 96 patients, although no treatment was reported.
- Damage to the joints of the lower jaw is necessarily combined with an exacerbation of the disease. It is characterized by the involvement of typical joints in the pathological process - interdigital and wrist.
- There is symmetrical inflammation that develops on both sides simultaneously.
- The pain is of a typical inflammatory nature, intensifying in the second half of the night and in the morning. Therefore, patients may be bothered by morning stiffness when chewing, which prevents them from having a normal breakfast.
- Anterior to the auricle there will be redness of the skin and painful swelling, which is located just above the joint. Due to such symptoms, the appearance of the patient’s face during an exacerbation takes on a characteristic appearance.
A characteristic feature of the disease is that the symptoms are always relieved after the patient takes anti-inflammatory drugs. Lifelong treatment in such patients helps prevent the development of exacerbations, which each time involve more and more joints.
In the third article of this group, pain during contraction of the massage muscle on each side was measured using a pressure algometer applied to the muscle belly. It is unclear how the subgroup of 55 patients was selected from a total of 110 patients. Without exception, the results of three studies showed that acupuncture is effective. The benefits of acupuncture appear to be comparable to those of combining standard therapy with plaque occlusion or plaque occlusion alone. Pain and joint function seem to respond.
According to these data, the effect appears to remain stable up to 1 year after therapy. No tests have been performed to control for the placebo effect of acupuncture. However, these results should be interpreted with caution. It is noteworthy that all studies come from Scandinavia, studies should be conducted in other areas to increase reliability. Most importantly, none of the studies were designed in such a way that the placebo effect could not be excluded from the mechanism of action.
Traumatic arthritis

Symptoms of dysfunction can be observed with acute damage to the joint - when it is subjected to excessive stress. This occurs when there is a strong blow to the jaw, a sharp forceful opening of the mouth, or an attempt to chew on a hard object. Signs in this case appear instantly, based on displacement of the articular surfaces:
Acupuncture is almost certainly associated with a powerful placebo effect, perhaps because it is invasive, mildly painful, exotic, and labor-intensive. One way to study this is to do a control group with sham acupuncture: needles are inserted at points without acupuncture. This process is usually indistinguishable from actual acupuncture. Patients may soon be blinded to their expectations of the treatment being evaluated. It is difficult to understand why such a test, which is ethically more justifiable than no treatment control, has never been performed.
Possible mechanisms for short-term pain relief include decreased inhibitory control with central release of opioids along with norepinephrine and serotonin in posterior horn spinal cord. Permanent relief may involve various mechanisms, such as increased blood supply and local secretion of calcitonin gene-related peptide. Improving blood circulation can help repair dysfunctional muscles, as evidenced by muscle relaxation.
- A sharp attack of pain immediately develops, intensifying with any attempts to move the lower jaw. It has a shooting character, starting from the ear area and extending to the chin.
- The mouth is slightly open or slightly skewed to the side, which is associated with a dislocation. A sharp muscle spasm does not allow you to close it on your own - if you try to do it with your hand, the jaw will instantly return to the same place.
- In this case, speech becomes impossible - the victim makes only “mooing” sounds.
- Since the functioning of the tongue and cheeks is disrupted, salivation is observed from the corners of the mouth.
This form is the most favorable for prognosis, since all symptoms are completely reversible. The inability to speak and eat food forces the patient to seek treatment, the essence of which is to set the jaw back.
Usage computed tomography for the diagnosis of the temporomandibular joint. To evaluate tomographic images, it is necessary for the professional to know the sectional anatomy of the articular region so that he can recognize structural changes. Thus, in this work, tomographic characteristics of normality, morphological changes and pathological conditions, most often found in the area of the temporomandibular joint.
Key words: Diseases of the temporomandibular joint; Tendon syndrome syndrome; CT; Diagnosis by image; osteoarthritis; Bone diseases. The temporomandibular joint is often studied in the field of speech therapy because it is responsible for the movement of the lower jaw and the effectiveness of dental functions. Bony structures - head of the condyle, glenoid fossa and articular eminence temporal bone. Components soft fabric are the masticatory muscles, articular ligaments, articular discs and articular capsules.
Chronic subluxation
This lesion is essentially reminiscent of deforming arthrosis - only it develops not in the knee or spine, but in the jaw area. It is based on long-term and continuous damage to the temporomandibular joint, which leads to the destruction of its components. Therefore, you should not joyfully crack nuts with your teeth - over time, this can lead to dysfunction. Here the pathology is characterized by the following signs:
Temporandibular dysfunctions affect the dental system as a whole, making it suitable for these people, depending on each individual's physiological tolerance. The causes and pathogenesis of temporomandibular joint disorders are multifactorial, including psychological, behavioral and environmental factors. Other causes include local trauma or procedures that cause joint stress.
Clinical examination is of great importance for the diagnosis of temporomandibular disorders, but its limitations are due to the difficulty of standardizing its criteria, which leads to doubts in interpretation. It is in this context that image verification is needed, which provides important additional information to get a diagnosis.
- Pain occurs only after intensive work of the jaws - eating hard food. They are aching in nature and are located in front of the ears. Because of this, they are often confused with headaches.
- The next symptom is restriction of mouth opening when a person is in pain or finds it difficult to do so. Therefore, the disease is often detected at a dentist's appointment - there you need to sit for a long time with your mouth wide open.
- While eating, you may notice a distinct crunching sound, felt at points just anterior to the ears. It can also resemble a creaking sound, which the patient himself hears in complete silence when clenching his jaws.
- The shape of the face gradually changes - smoothing of the chin and cheeks is noted, which is associated with a decrease in the tone of the masticatory muscles.
The symptoms are caused by already persistent changes in the jaw joints, which makes it difficult conservative treatment such patients, making surgery the method of choice.
To evaluate tomographic images, it is necessary for the examiner to know the sectional anatomy of the articular region so that he can recognize structural changes and pathological conditions. Therefore, the tomographic characteristics of normality, morphological changes and pathological conditions most commonly found in the temporomandibular joint region will be revealed and described in this study in addition to the related information of some.
Presentation of clinical cases. In its normal aspect, the mandibular condylar process acts as a site of adaptive growth even under the functional load supported by its cartilage. The morphology of the mandibular condyle is characterized by a rounded bony projection with a superior oval and biconvex surface in the axial plane. Typically, the anteroposterior dimension is smaller than the medial side, the ends of which are called the lateral and medial poles.
Treatment
The tactics for helping each patient are based entirely on the results of the examination. Sometimes a thorough examination is enough to confirm the inflammatory nature of the dysfunction. Just in case, each patient undergoes an X-ray examination to rule out injury.
Figure 1: Tomographic reconstruction of closed mouth sagittal sagittal open mouth and coronal with right side, demonstrating an aspect of normality of the temporomandibular joint. Note the cortical bone covering the entire condyloma. Already in the sagittal reconstructions the closed mouth, sagittal open mouth and coronal on the left side show planing, indicated by black arrows.
It is characterized by changes in fibrous tissue adhesion with adjustments to the bone of the condyle, glenoid fossa, zygomatic arch, and in some cases, coronoid process mandible, promoting calcification of these structures with limitation of mouth opening and jaw mobility, often without symptoms and pain.
Dysfunction can also be treated at home if the patient fully follows all the doctor’s recommendations.
For any person, this becomes unbearable torment, since for at least one week he must eat only liquid food. In severe cases, this has to be done through a tube to prevent any movement in the joint. And since the patient’s activity is almost unimpaired, he doesn’t want to stay in the hospital at all.
But this may be necessary if the patient is to undergo surgery - then constant monitoring is vital. And after any treatment method, rehabilitation is performed to return normal chewing function.
Conservative
When choosing this technique, doctors always rely on recent changes in the joint that can be easily reversed. Therefore, they include the elimination of inflammatory signs, as well as therapeutic immobilization:
- Measures begin with adequate pain relief to eliminate spasm of the masticatory muscles. For this, novocaine blockades are often used, which eliminate the mechanical component of pain.
- If the cause is acute injury, then manual reduction of the jaw is performed. The sooner this procedure is performed, the lower the risk of further complications.
- Then therapeutic immobilization is performed - a tight bandage or plaster splint is applied to the lower jaw. They prevent any movement in the joint that will cause symptoms to return.
- To eliminate inflammation, special medications are prescribed in the form of injections that reduce swelling of the tissues surrounding the joint.
- At rheumatoid arthritis hormones and drugs that inhibit activity are prescribed immune system. At the same time, its aggressive effect on cartilage and articular membranes is eliminated.
Therapy lasts at least two weeks, after which patients begin restorative procedures.
Surgical
With the protracted course of any disease of the temporomandibular joint, its gradual destruction occurs. That's why conservative methods will be ineffective - prolonged immobilization will only aggravate the pathological changes. To eliminate them, use the following operations:
- The first type of intervention is aimed at creating a new head of the lower jaw. It is recreated from the patient’s own tissues or an artificial prosthesis is used.
- The second type of surgery involves deepening the articular cavity, which has become deformed as a result of arthrosis. To do this, all altered tissues are removed, and an artificial surface is installed in their place. It can also be created from the patient's soft tissue.
In any case, the operations will only be of a facilitating nature, without completely returning the function in the joint. They are needed only for the patient’s normal self-care, so that he can eat normally. Some restriction in mouth opening still remains, which leaves problems with speech.
Rehabilitation
Recovery time depends on the amount of treatment performed; during operations, it can take up to several months. Again, rehabilitation will not return the patient’s jaws to their former characteristics, but will only adapt them to normal operation. Methods include physical therapy and adherence to certain rules:
- To speed up healing and reduce the volume of the scar, laser and electrophoresis with enzymes are used on the area jaw joints. Their purpose in early dates helps prevent the development of adhesions, which will then limit the opening of the mouth.
- During the first month, rough chewing movements are excluded - all food should be semi-liquid and pureed. In their free time, patients are recommended to wear rubber pads to prevent complete clenching of the jaws.
- Applicable physical therapy aimed at increasing volume passive movements. Active gymnastics is prohibited until the patient has fully recovered.
Even after successful treatment, physical restrictions on the jaw joints must be observed. Many people believe that if the symptoms have disappeared, then the disease is completely defeated. But the pain can return with any injury or excessive chewing stress - so recent patients should avoid such situations.
Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint in medicine has several names: arthrosis of the TMJ joint, arthritis, chronic subluxation of the lower jaw, myofascial syndrome, and so on. The first person to study this pathology was the American otolaryngologist Kosten. It was he who discovered the connection between ear pain and dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. As a result, the disease acquired another name: It is worth noting that such a pathology is considered the most painful and complex, since it is difficult not only to diagnose, but also to treat.
Features of the joint
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is located in front of the ear. He plays an important role. The joint consists of the bones of the lower jaw and the temporal bone. At the same time, his muscles perform many functions: speech, swallowing, chewing, and so on. In addition, they connect the skull to the lower jaw. Muscles and joints allow a person to open and close their mouth. The device is also responsible for the movement of the lower jaw to the right, left, forward, down and up.
What is TMJ dysfunction
Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, the treatment of which has its own characteristics, manifests itself when symmetry is disturbed. The device works correctly as long as everything moves the same way on both the right and left. If a malfunction occurs in one joint, then a violation of symmetry occurs, which leads to dysfunction of the second joint. Pathology begins to develop in cases where the lower jaw moves when closing and opening the mouth, and then when moving in other directions.
Main causes of pathology
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction syndrome occurs in patients of various age groups. Statistics show that approximately 70% of the population suffers from such disorders. There are plenty of reasons for the development of pathology. Among them are:
- stress;
- malocclusion;
- sudden muscle strain when grinding rough and hard food;
- increased abrasion of dental tissues;
- physical activity and training during which a certain muscle group is tense;
- mistakes made by dentists, surgeons, therapists, orthodontists, orthopedists: fillings, dental prosthetics;
- injuries of the joints of the lower jaw.
When filling or prosthetic teeth, a specialist can install an oversized crown or filling. As a result, symmetry is broken. And this, as is known, leads to the development of dysfunction of the temporomandibular joints. In addition, with such improper treatment, the load falls on only one side of the teeth when chewing food, which leads not only to disc displacement, but also to pain. 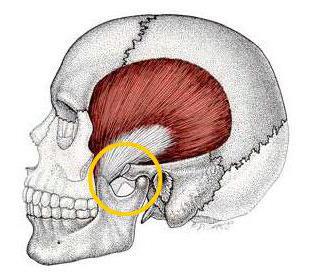
Noise and clicking
How does temporomandibular joint dysfunction manifest? The symptoms of this pathology are very diverse. The most common sign of this pathology is clicking sounds that are heard in the joints of the lower jaw. Such sounds can be quite loud. They can be heard by people who are close to the patient when he simply opens his mouth, yawns or chews food. At the same time painful sensations may not occur.
As a rule, when the discs are displaced, muscle strain occurs when the patient hears a click. This usually happens when chewing food. At such moments, the patient may feel pain in the neck, head, and face due to tension.
Headache
Temporomandibular joint pain dysfunction syndrome often manifests itself as pain in different areas of the head. This is another common sign of pathology. Usually headache with the development of dysfunction, the TMJ is localized in the area of the back of the head and temples. But often the patient may experience discomfort in the area of the shoulder blades.
The cause of the headache in this case may be muscle pain, which occurs when grinding teeth and clenching the jaw. Also, discomfort may bother the patient due to displacement of the discs of the joint itself. In this case, pain radiates to the neck, forehead or temples. It is worth noting that such unpleasant phenomena can be quite strong. In some cases, the doctor mistakenly diagnoses brain pathology or migraine. 
Locking, gripping a joint: locking
Painful dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint often causes uneven movement of the lower jaw due to certain disorders. Blockage may be noticed when opening the mouth. There is a feeling that the patient is trying to “catch” something with the lower jaw.
In some cases, people with a blocked joint need to move the device left and right to open their mouth wider. But there are other situations. Sometimes the patient is forced to open his mouth until a peculiar click is heard in the area of the joint with impaired functions.
Ear symptoms
Since the TMJ is located very close to ears, certain ear symptoms may occur. Some of them are quite unpleasant. Signs of dysfunction in this case include:
- pain;
- feeling of ear fullness;
- dullness in the ears causing hearing loss.
It is because of these signs that many patients who have temporomandibular joint dysfunction seek help from a local physician or ENT doctor. 
Dental problems
Malfunction of the joints of the lower jaw can lead to changes in bite or dental occlusion. This often happens due to disk displacement. The bones and their connections do not correspond to the norm, which leads to a change in the bite.
In addition to this problem, the patient's teeth may become very sensitive. This most often occurs due to teeth grinding and jaw clenching. Often people with this pathology turn to dentists with complaints of pain in their teeth. It is not always possible for specialists to determine the main cause of the occurrence. discomfort. Because of this, the patient may have the tooth removed or have it depulped. But this does not save you from TMJ dysfunction.
Other signs
Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint in certain situations is accompanied by inflammatory processes resulting from synovitis or arthritis in the joint itself. In this case, a person may complain of tissue swelling and pain. This often leads to general malaise, weakness and fever.
In addition to the above symptoms, the patient may be concerned about:
Initial diagnostic stage
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction has many symptoms. However, diagnosing such a pathology is a multi-stage, lengthy, complex and complex process. It is not always possible to make a correct diagnosis based solely on the patient’s complaints. First of all, it is performed functional diagnostics, which allows you to determine the causes of the development of pathology.
In this case, a set of procedures is carried out:
- collection of medical data;
- identification of all complaints;
- examination of the muscle tissue of the neck and head;
- X-ray diagnostics: magnetic resonance and cone beam tomography;
- neurological examination, lateral teleradiography;
- cephalometric analysis;
- identification of parafunctions;
- occlusion.
Dental examination
In some clinics, a small functional dental analysis is often performed to determine the diagnosis. This is also considered the primary diagnosis. In this case, an impression is taken from the patient, and then a model is made. Also, special drops are used for diagnosis, which help identify bruxism. During the examination, the dentist must evaluate the bite, as well as the quality of interdental contacts, etc.
Large functional analysis is considered the most difficult, not only in implementation, but also in data interpretation. In this case, the specialist must have special skills and knowledge. To carry out such diagnostics, additional equipment is required.
All of the above tests are necessary to make a diagnosis and identify the causes of TMJ dysfunction. The accuracy of the studies performed depends on the experience of specialists and equipment. After diagnosis, the patient is prescribed adequate therapy. It, in turn, can be surgical, reconstructive or conservative. 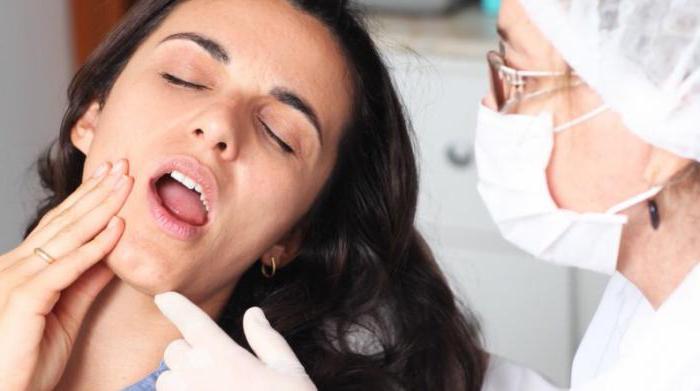
Who to contact
This pathology is quite difficult to diagnose. Even experienced dentists rarely make a diagnosis of temporomandibular joint pain dysfunction. Treatment in many cases is prescribed incorrectly and does not produce results. In most cases, patients do not receive qualified help from dentists and begin to visit other specialists: psychotherapist, neurologist, therapist, otolaryngologist, chiropractor, osteopath, and so on. In reality, it is dentists who should treat dysfunction.
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction: how to treat
To get positive result, complex therapy should be carried out. It includes orthopedic treatment dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, which is aimed at correcting the bite. In certain situations it is carried out surgery, acupuncture, physiotherapeutic procedures, dental prosthetics or removal and installation of a new filling.
In addition to the above, your doctor may prescribe wearing a trainer at night. This is a kind of joint splint that allows you to relieve pain. It is also used for diagnostics and to prevent abrasion of dental tissues during bruxism.
Can temporomandibular joint dysfunction cause complications? Treatment of such a pathology must be carried out without fail. In some cases, the dysfunction leads to disc displacement. As a result, the surfaces of the joints are susceptible to restructuring - arthrosis. Connective tissue, which itself is rough, begins to grow in the cavity. As a result, the joint stops moving. This pathology is called ankylosis.
How to give first aid
If the patient is completely sure that he has dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, then, if necessary, you can help the patient by reducing pain and also improving chewing function. To do this you need heat, but only moist. In this case, you can apply a compress to the sore spot: a bottle pre-filled with hot water. To avoid burns, it is recommended to wrap the container in a slightly damp, but not wet, towel.
To reduce the intensity of pain and also reduce inflammation, it is recommended to use ice. In this case, you can use a bag or bottle. However, you should not apply such a compress directly to skin. The package or bottle should be wrapped in a towel. It is not recommended to use it for longer than 15 minutes. In this case, the break between procedures should be at least 60 minutes. Analgesics can temporarily relieve pain. 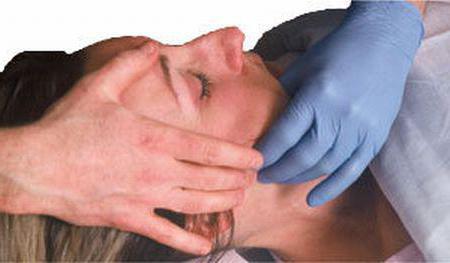
How to relax a joint
To prevent the joint from straining frequently, you should follow several rules. Food should be pureed or soft, as well as mixed. It is worth avoiding chewy, rough, hard and hard foods. You should bite off in small pieces. With this disorder, it is not recommended to open your mouth wide.
Relaxing your body completely also helps reduce pain. Any relaxation technique will work for this.
Painful dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint: ICD-10
According to international classification diseases, dysfunctions of the temporomandibular joint are indicated by code K07.6. In this case, violations can manifest themselves in different ways. These include: complex or Costen syndrome, TMJ looseness, “clicking jaw”, TMJ lobar dysfunction syndrome.
Exceptions are stretching and
