Rocket and aircraft designers can accurately name the number of parts that make up an aircraft, down to the smallest screws. The creators of computers know every chip in their brainchild. And only medical scientists have not come to a consensus about the number of bones in the human skeleton.
The fact is that the number of bones depends on individual features a person and may differ due to the presence of additional, the absence of a part of small bones or the fusion of several into a single whole.
 The human skeleton is a flexible framework consisting of solid formations (bones) and their connections (joints and ligaments). The skeleton determines the shape of the human body and serves as its support.
The human skeleton is a flexible framework consisting of solid formations (bones) and their connections (joints and ligaments). The skeleton determines the shape of the human body and serves as its support.
Muscles are attached to it that can contract, which makes it possible for a person to move.
For many centuries, bones were considered inanimate, performing only mechanical functions. Now scientists know that bones are living formations that are constantly being updated, rebuilt and have their own blood vessels and brain.
Based on this understanding, the functional purpose of the skeleton is much broader than previously accepted.
The skeleton is designed to perform the following functions:
- serve as a mechanical support for soft tissues and a place for their attachment;
- provide body mobility as a result of muscle contraction and relaxation;
- provide flexibility of the body due to joints and ligaments;
- protect vital organs rib cage designed to protect the heart, lungs, bronchi, esophagus, liver and spleen; skull - the brain, pituitary gland and pineal gland; spine - spinal cord; pelvic bones - reproductive organs);
- accumulate and maintain reserves of calcium, phosphorus and iron necessary for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles;
- work out various forms blood cells in the bone marrow filling the cavities of cancellous bone tissue.
Total
This question has worried healers since ancient times. The ancient healers of Tibet counted 360 bones. Sushruta, a surgeon from ancient India, believed that the number of bones ranged from 300 to 306. One of the apocrypha of the XI century states that there are 295 bones. The Vikings numbered 219.
Modern anatomy textbooks generally do not name the exact number of bones in the skeleton, indicating their approximate number: “about two hundred”, specifying the range of 208-210 bones. Most scientists stop at the numbers 206 and 207.
The bones of the human skeleton have amazing strength at a relatively low weight due to the hollowness of their structures.
If the skeleton were made of steel, then its weight would reach 240 kg. And its weight is only one fifth of the weight of the body, while maintaining huge loads: when stretched, the bone can withstand a force of at least 1800 kg/cm2, when compressed it can withstand pressure up to 5400 kg/cm2, and the femur of a long jump athlete can withstand a load of 9000 kg.
 Everyone at school had a skeleton, and it would seem that there is nothing easier than counting the bones for him. But it was not there. Twenty percent of people with disabilities in the development of the musculoskeletal system confuse all the calculations.
Everyone at school had a skeleton, and it would seem that there is nothing easier than counting the bones for him. But it was not there. Twenty percent of people with disabilities in the development of the musculoskeletal system confuse all the calculations.
But even here there are discrepancies. The second half of scientists believe that there are 207 bones. Why not find it, this “bone of discord”?
In adults
There are many mysteries in the adult human body.
Every fifth has deviations in the number of vertebrae in the lumbar and cervical regions, and every twentieth has an extra rib.

In some, some of the bones grow together over time, and in some, they do not. The sacrum in most cases consists of five fused vertebrae, but scientists have not agreed on whether to count it as five bones or one.
For now, it is worth accepting the statement that an adult has about two hundred bones: the two most probable numbers are 206 and 207.
The difference in the number of bones is not always congenital.
During the formation of the skeleton, the number of its bones may change due to a decrease in the number of cervical vertebrae to six due to the fact that the seventh cervical vertebra can be assimilated by breastfeeding.
The number of thoracic vertebrae can decrease to eleven, and the lumbar vertebrae can increase to six or decrease to four.
Another proven way to treat diseases of the joints and spine is the Kuznetsov applicator. In what cases it can be used, find out.
In children
In a child at birth, the number of bones is also determined in different ways.
Most doctors believe that there are 300 of them, but there are those who believe that there are 270 and 350.
With this, everything is just clearer - the bones of the baby are very small, and it remains to agree on starting from what size they should be counted. But everything is not so simple.
Babies are born with different weights, and a premature baby can have bones far below the minimum limit. Of course, we can agree that the number of bones in a baby weighing 3 kg and 50 centimeters tall is taken as the standard, but this will also have a large share of conventionality.
Given all the factors, scientists call the approximate number of bones of a newborn baby - 300.
The fetus of a baby has within a few weeks a rudimentary tail of separate bones, which then grow together and turn into a coccyx.
At birth, the bones of a child are flexible and soft, otherwise the baby could not be born. The cartilaginous skeleton of the fetus in the prenatal period gradually turns into bone. This process continues for several years after birth.
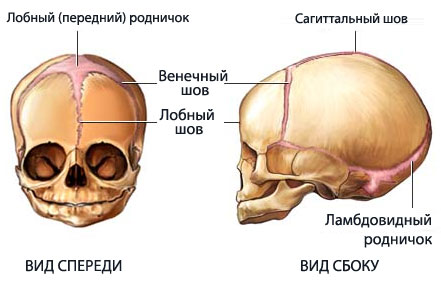
Figure: Child's skull
As the child grows, some small bones grow together until their number reaches 206 or 207 bones. Such fusion for different bones lasts different times.
The bones of the baby's skull are not fused and the "fontanelles" between them, consisting of connective tissue, are overgrown with bone tissue by about two years.
The vertebrae of the sacrum fuse completely into a single bone only by the age of 18-25.
How many pairs of bones are there in our body?
The human skeleton is symmetrical with respect to the spinal column, and therefore most bones are paired.
In total, there are 86 pairs of identical bones in the body, or 172 pieces:
- 8 pairs refer to the bones of the head;
- 12 pairs make up the ribs;
- the upper limbs (except for the hands) consist of five pairs;
- hands consist of 27 pairs;
- the lower limbs are made up of 34 pairs.
Number by department
With regard to paired bones, there are no differences of opinion on their number. This means that the “bone of discord” is among the unpaired ones.
Indeed, the spinal column, according to various sources, consists of 33 or 34 vertebrae.
There is no disagreement about the upper sections of the spine, but in the coccygeal section of the spine, four or five vertebrae are indicated, depending on the degree of development of our “tail” and the presence of a rudimentary fifth vertebra in it.
It can be assumed that 206 is the same as 207 "with a tail". But listing all the bones of the skeleton really gives the number 211 (without a tail) or 212 (with a tail).
It should immediately be noted that six bones (three pairs) of bones of the middle ear that are not connected to the skeleton do not participate in the calculations, and the spine is considered from 34 vertebrae.
The skeleton is usually divided into axial and additional sections. The bones of the head, face, neck, and trunk (skull, spinal column, sternum, and ribs) are axial department, and the bones of the shoulder and pelvic girdle and limbs belong to additional departments.
So, we use two methods for recalculating bones:
- sum up the paired (172) and unpaired bones (40) and get a total of 212;
- sum the bones axial skeleton(80) and bones of the limbs (10+54+68) and we get a total of 212.
If we subtract 207 (with a tail) from the resulting sum of 212 (with a tail), then we get 5 extra vertebrae.
It is 5 sacral bones that grow together and usually appear in the calculations as a single bone.
It would seem that everything converges, but inquisitive minds have already noticed the catch. And rightly so. After all, subtracting 207 bones into which the sacrum entered as a single bone, we also subtracted it, although it was not included in our number! So, we need to add one bone to our result.
We will have to apply the third method - the method of direct recalculation of the bones of each section and subsection of the spine with their subsequent summation.
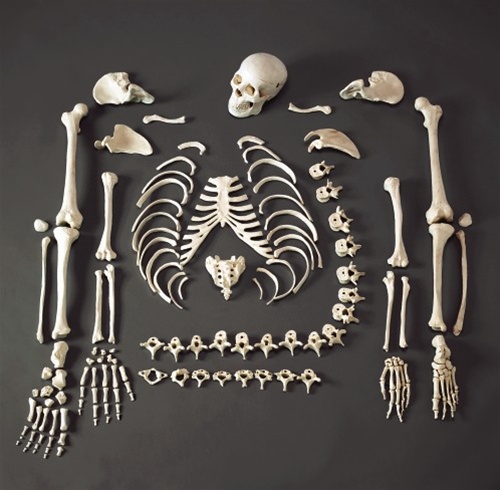
To count the bones in the third way, we present the complete structure of the human skeleton.
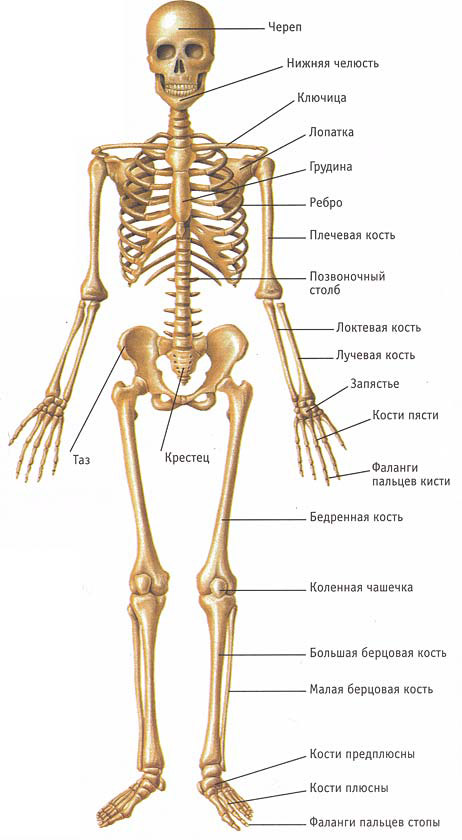
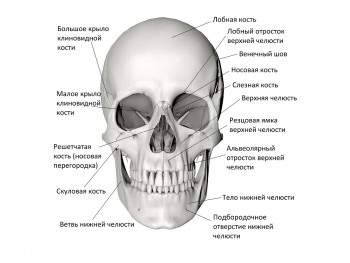
human skull
There are 23 bones in the skull (8 of the brain section and 15 of the facial section).
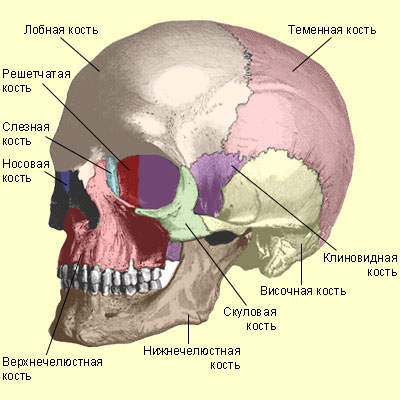
Figure: human skull
Brain bones include:
- frontal;
- 2 parietal;
- occipital;
- wedge-shaped;
- 2 temporal;
- lattice.
There are 15 facial bones:
- 2 bones of the upper jaw;
- 2 palatine;
- coulter;
- 2 cheekbones;
- 2 nasal;
- 2 lacrimal;
- 2 inferior turbinates;
- lower jaw;
- hyoid bone.
There are only two nasal bones, the rest of the nose is formed by cartilage.
torso
There are 32, 33 or 34 vertebrae in the spine:
- 7 cervical;
- 12 chest;
- 5 lumbar;
- 5 sacral, counted as one bone;
- 3-5 coccygeal.
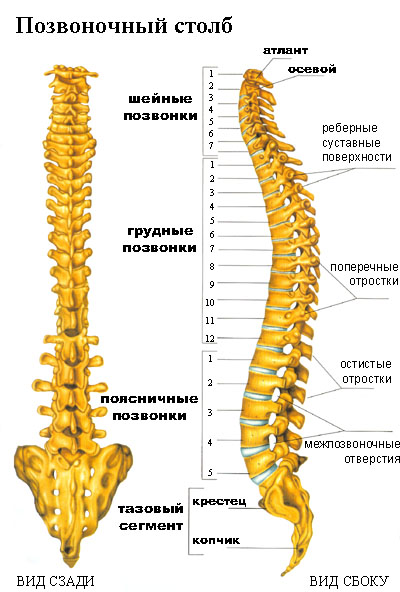
Figure: spine
It seems that somewhere in the coccygeal region, the missing vertebra in our calculations is hiding. It turns out that they can appear in the calculations not only 4 or five, but also three.
But for now, you should continue counting the rest of the bones of the body.
The chest, not counting the thoracic vertebrae, has 25 bones:
- 24 ribs,
- sternum.
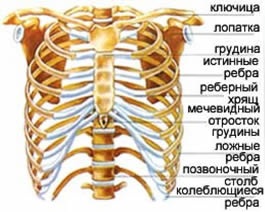
The girdle of the upper limb consists of 4 bones:
- 2 spatulas,
- 2 clavicles.
Number of bones in a person's hand
Free parts upper limbs are made up of 6 bones:
- shoulder (2 humerus);
- forearm (2 ulna and 2 radius bones).
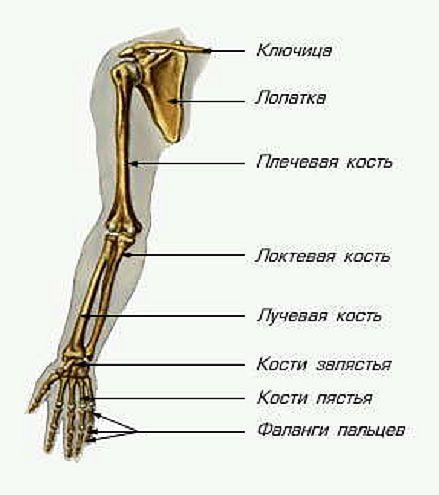
Figure: hand bones
The brush consists of 54 bones (27x2):
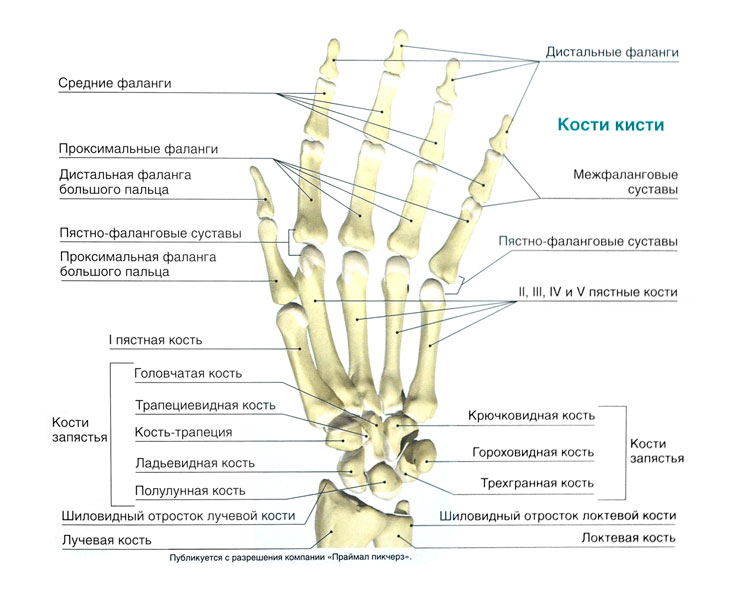
Figure: hand bones
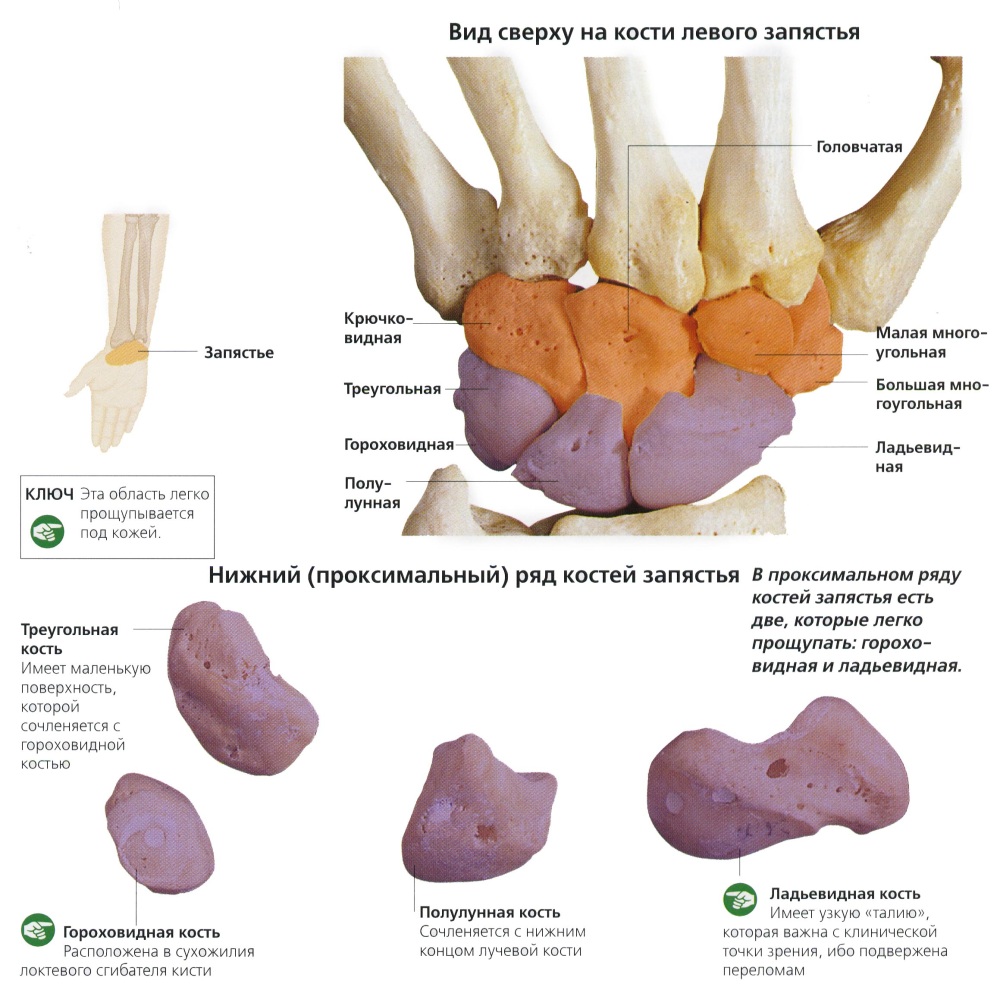
Wrist - 16 bones:
- 2 navicular,
- 2 lunar,
- 2 trihedral,
- 2 peas,
- 2 trapezoid bones,
- 2 trapezoidal,
- 2 capitate bones,
- 2 hooked.
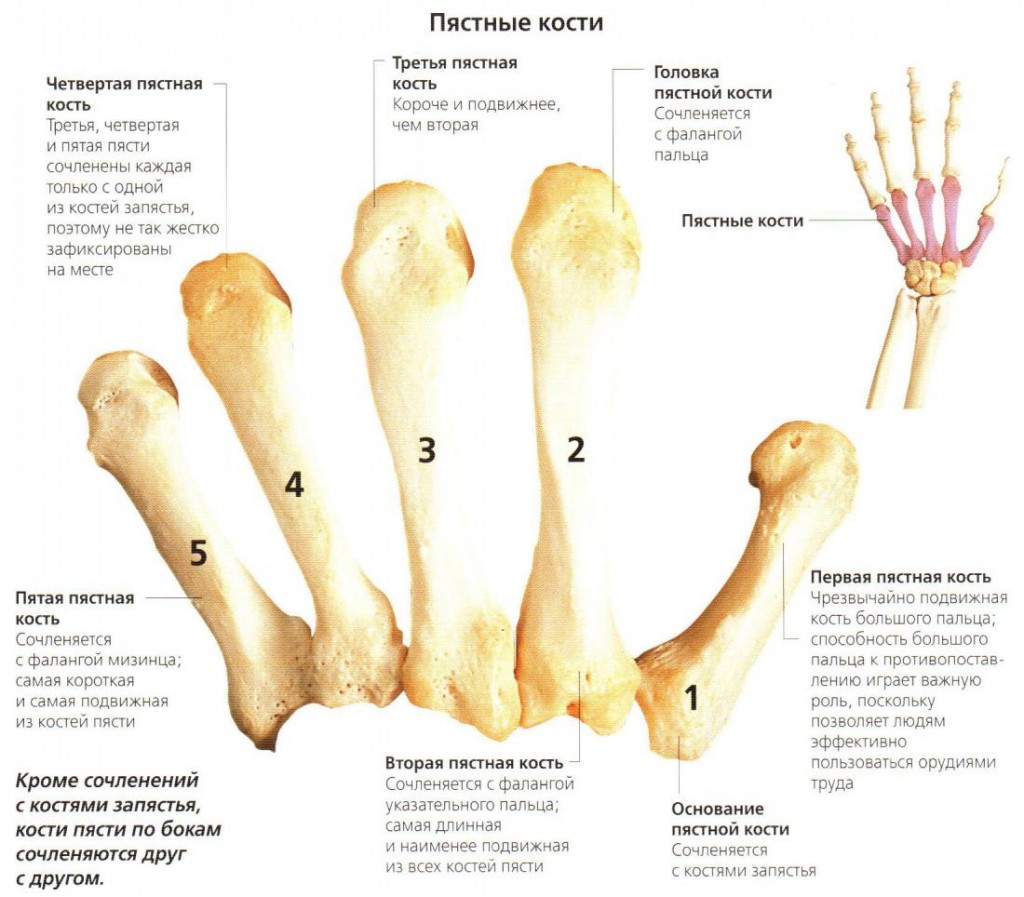
- metacarpal bones;
- bones of the fingers (10 proximal phalanges, 10 distal phalanges and 8 middle phalanges, as in thumbs middle phalanges are absent).
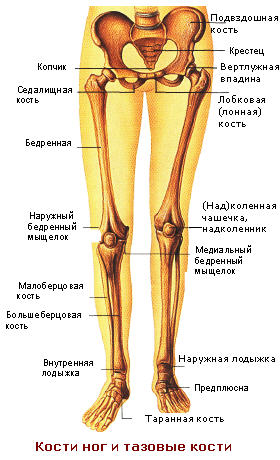
Number of bones in the leg
The free parts of the two lower limbs consist of 60 bones:
- thighs (2 femoral and 2 patellas),
- lower legs (2 tibial and 2 fibular),
- 52 foot bones (26x2): 14 tarsal bones, 2 calcaneus bones, 2 talus bones, 2 navicular bones, 2 medial cuneiform bones, 2 intermediate cuneiform bones, 2 lateral cuneiform bones, 2 cuboid bones, 10 metatarsal bones, and 28 finger bones.
The number of paired bones is indicated in total for both limbs for ease of calculation.
There is only one bone in the human heel - the calcaneus, the most big bone foot, and on it is the Achilles tendon, three articular surfaces, the sinus of the tarsus, the support of the talus and the groove with the tendon of the fibula.
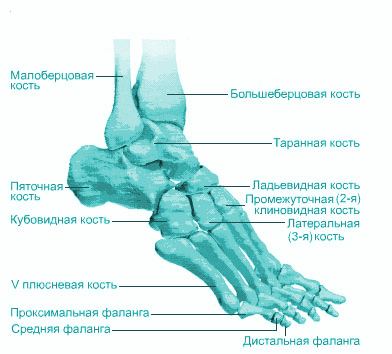
Figure: foot bones
Counting the total number of bones at 3, 4 and 5 coccygeal vertebrae gives 210, 211 and 212 bones, respectively. If five sacral bones are counted as one (that is, subtract five and add one), then we get 206, 207 and 208 bones, respectively.
Video: functions, structure and development of the human skeleton
Structure and composition
Light but strong as steel, bones consist of a hard material (matrix) with scattered bone cells (osteocytes) in it.
The matrix consists of 2 main components: collagen protein, which gives it flexibility, and mineral salts such as calcium phosphate, which give strength.
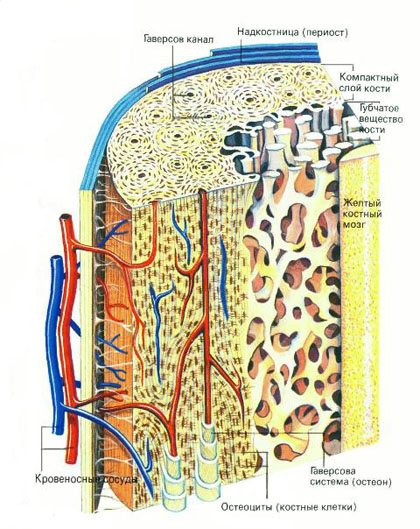
Fig.: bone structure
The matrix in the bones is presented in the form of a solid compact substance (outer layer) and in the form of a spongy substance (inner layer).
Long tubular bones have a central cavity filled in adults with yellow bone marrow, in which fat is deposited. In the ribs, sternum, vertebrae, pelvic bones, skull and ends of tubular bones is located red Bone marrow that produces white and red blood cells.
According to the size and shape of the bones are divided into four types:
- long, including tubular, bones (for example, the femur);
- short (for example, the bones of the wrist);
- flat (for example, ribs);
- bones of an irregular shape (for example, vertebrae).
Video: bone structure
Connection types
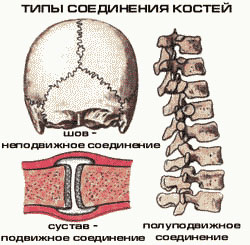
The school curriculum divides all bone joints into fixed, semi-movable and movable.
motionless
Sometimes the bones grow together or the protrusions of one bone rigidly enter the recess of the other. At the same time, there is no mobility at the place of articulation (seam).
This is how the bones of the brain part of the skull are connected.
semi-movable
The semi-mobility of the bones is provided by elastic cartilaginous layers between the bones. Such connections are characteristic of the spine. During movement, the cartilages between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers, protecting the body from sudden shocks and tremors.
Movable
Movable joints of bones are called joints. They provide movement of body parts in different directions.
Joints are made up of smooth cartilage articular surfaces articulating bones, articular bags (capsules), articular cavities and auxiliary elements: ligaments and tendons.
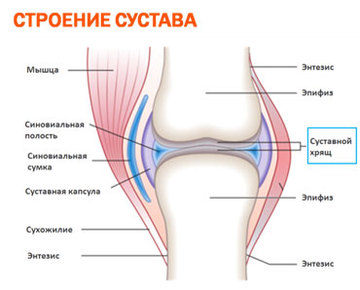
Fig.: the structure of the joint
Joints are simple and complex. In simple joints, two bones are connected, and in complex joints, three or more.
Examples of simple joints are hip joints and joints of the phalanges of the fingers, and examples of complex ones are the knee and elbow.
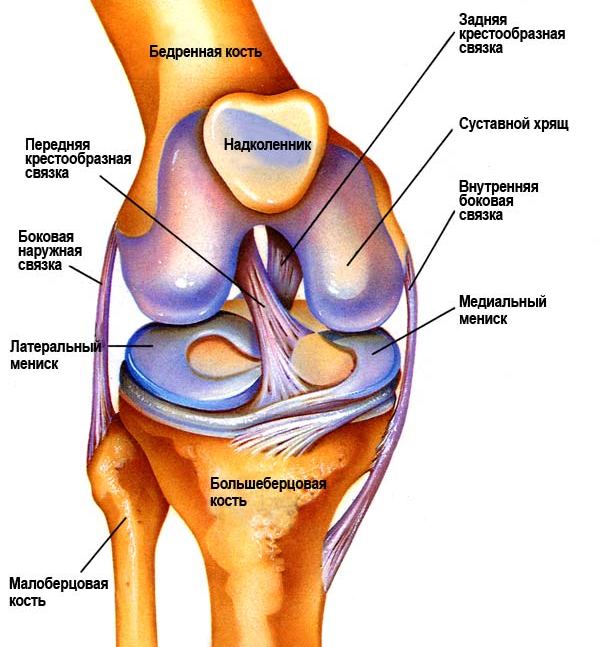
Rice.: knee-joint
medical science classifies bone joints somewhat differently:
- continuous, occurred due to the fusion of bones;
- discontinuous (joints), providing differentiated mobility of various bones of the skeleton;
- semi-joints, an intermediate type between the first two.
On closer examination, it is noticeable that both classifications with different names coincide in essence.
Scientists have learned to restore the face of long-dead people from the bones of the skull. Previously, this was done with clay, but now computer graphics are used.
Thanks to this, we can find out what our ancestors looked like. But it turns out that the bones of the skeleton can tell a lot more.

Criminalists and archaeologists determine the gender and age of people who have gone to another world by bones.
Age determination
Forensic experts determine age by the degree of ossification of bone cartilage:
- At the age of 15, the formation of the foot ends;
- at the age of 25, the sternum fuses with the collarbone;
- at 40, 75% of the bones of the skull fuse.
- the pelvic bone in a child consists of three bones with a cartilaginous layer, and by the age of 15-16 they grow together into one.
These signs do not allow us to give an absolutely accurate answer. Apart from these, there are other age features human skeleton.
Modern archaeologists and anthropologists use R. Martin's scheme, which determines age categories.
1. Children's age:
- early childhood - before the appearance of the first permanent teeth (6-8 years);
- late childhood - before the appearance of permanent second molars, or before the onset of puberty (from 6-8 to 12-14 years).
2. Adolescence- until the wedge-occipital suture is overgrown, that is, from 12-14 to 20-22 years.
 3. Age of manhood- from the appearance of the third permanent molars and the beginning of overgrowth of the cranial sutures to the average wear of the teeth (from 20-22 to 30-35 years).
3. Age of manhood- from the appearance of the third permanent molars and the beginning of overgrowth of the cranial sutures to the average wear of the teeth (from 20-22 to 30-35 years).
4. Mature age with an average degree of overgrowth of cranial sutures and severe tooth wear (from 30-35 to 50-55 years).
5. Elderly age with complete overgrowth of cranial sutures and severe wear and loss of teeth (from 50-55 years).
The age of adolescents and children is determined to the nearest year by the timing of ossification of the skeleton, the timing of teething, and the size of the bones.
During normal development:
- from 2-3 months the anterior crown of the skull closes;
- by 1.5 - 2 years, the posterior crown is closed, the metopic suture is still preserved on the frontal bone, and the milk teeth have just erupted or have not yet erupted completely;
- a more accurate age of the baby is determined by the number of cut milk teeth;
- by the age of 3-6, the first molar tooth (molar) appears and all parts of the spinal column grow together;
- from 7-8 to 12-14 years, most of the teeth erupt;
- by the age of 14-16, three pelvic bones fuse into one;
- by the age of 15-18, the lower thickened end of the humerus and the upper thickened ends of the ulna and radius merge with the body of the bone;
- by the age of 17-20, the head and the lower thickened end of the tibia fuse with the body of the bone;
- by the age of 24-25, the formation of the skeleton as a whole is completed, and in women this process ends earlier than in men.
The biological age of an adult is determined with an accuracy of five years. This takes into account the timing of hardening of the cranial sutures, wear of the teeth, age-related changes in the skeleton (spinal vertebrae, heads of the humerus, etc.).
Each individual attribute gives a significant variation in determining age, but the combination of various attributes allows this figure to be made more accurate.
Sex determination
The easiest way to determine the sex of the bones of the pelvis:
- Women: pelvic bones wider and shorter than in men, their inner surfaces are even, and between them there is an oval hole, calculated in size and shape for the passage of the baby's head during childbirth.
- Men: the pelvis is narrower, the bones are more massive, and the hole between them resembles a heart in shape. The surfaces of the bones have hard protrusions that allow powerful muscles to be attached.
When determining sex, other structural features of the pelvis, skull and tubular bones are also taken into account.
The structure of the pelvis and tubular bones have the following gender differences:
- women have wings ilium deployed to the sides, and in men they are located more vertically, so the maximum distance between the iliac crests in men is 25-27 cm, and in women 28-29 cm;
- the male sacrum is longer and narrower than the female;
- the subpubic angle in women is straight or obtuse (90-100 degrees), and in men it is acute (70-75 degrees);
- the shape of the female pelvic cavity resembles a cylinder, and the male one resembles an inverted cone;
- long tubular bones in men it is heavier, longer and more massive than in women, which is especially noticeable in the structure of the femurs.
The structure of the male skull has the following gender differences:
- it is larger;
- has more pronounced reliefs in the places of attachment of muscles (superciliary ridges, bridge of the nose);
- the nipple-shaped process is wider (from 2 cm);
- the frontal and parietal bones are less pronounced;
- the forehead is more sloping;
- the fronto-nasal angle is better expressed;
- the lower jaw is more massive and larger;
- teeth large sizes roots are longer and wider.
The enumeration of the age and sex characteristics of the skeleton can be continued, but this is already a matter of the competence of professionals.

From this article, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- The skeleton of a person who did not have abnormalities during his lifetime consists of 206, 207 or 208 bones, depending on the number of coccyx bones. With an average number of coccyx bones, the skeleton consists of 207 bones.
- According to the human skeleton, you can determine the sex, age and restore the appearance of long-dead people.
Perhaps the majority wondered how many bones are in the human body. After all, thanks to them, the ability to perform certain movements and perform manipulations appears.
It turns out that their number in adults is less than in newborns. In addition, the number of bones depends on individual characteristics: someone's body has additional bones, and someone has fewer because some have grown together or are completely absent.
Scientists have not been able to reach a consensus on the number of bones in the body, so it is generally accepted that a newborn has about 350 of them, and an adult has 206-207.
The skull of a newborn is represented by separate parts, which are interconnected with the help of soft tissues (fontanelles). Gradually they close (usually by 2 years).
Some bones fuse over time (this process can continue until the age of 25). It turns out that at a young age and the elderly, their number is different.
The structure of the skull.
The skull consists of 3 sections:
- cerebral;
- facial;
- middle ear.
In some cases, people have extra ribs or fingers, as well as bones on the feet, growths on the fingers. Even in modern anatomy textbooks there is no exact number: it is succinctly reported that there are "about two hundred" of them. According to statistics, 20% of people have an extra rib.
The sacrum consists of 5 vertebrae fused together, but scientists could not come to a consensus: consider the sacrum as 1 bone or 5.
In the process of skeletal formation, the number of bones may change due to a smaller number of cervical vertebrae (when there are not 7, but 6). In the thoracic region, there may be fewer of them: 11 instead of 12, in the lumbar - 6 or 4 instead of 5.
Paired bones in the skeleton
How many bones are in the human body?
With respect to the spine, the skeleton is symmetrical, so many bones are paired:
- head bones include 8 pairs;
- ribs - 12 pairs;
- upper limbs - 5 pairs (excluding hands);
- hands - 28 pairs;
- lower limbs - 34 pairs.
Names of bones.
Considering that there are no “extra” bones among the paired bones, one should look for unpaired ones. According to various sources, in spinal column there are 33-34 vertebrae.
Some argue that the coccyx consists of 4 vertebrae, others - that of 5. In addition, 3 pairs of bones located in the middle ear are not taken into account, and they are not connected to the skeleton.
If you add paired and unpaired, 212 bones come out. If you count 5 sacral vertebrae as 1 bone, then the total number is 207. But this is not entirely true. There is another way to count. The skull includes 23 bones (15 in the facial and 8 in the brain).
Body Composition:
- 32-34 vertebrae;
- 24 ribs;
- 1 sternum;
- 2 clavicle bones;
- 2 spatulas;
- 2 shoulder elements;
- 4 forearm bones;
- 54 brush bones (27x2);
- 60 bones of the lower extremities.
In total, 210-212 bones come out (assuming that there are 3, 4 or 5 of them in the coccyx). Counting the vertebrae of the sacrum as 1, count 206-208. The given data does not allow to name the exact number. Many people believe that teeth are part of the skeleton. However, they do not apply to bones.
The smallest bone is the stirrup located in the middle ear, and the largest is the femur (its size is about 30% of a person's height).
Based on size and shape, there are 4 types of bones:
- long (tubular, including, for example, femoral), having a central cavity, in adults it is filled with bone marrow;
- short (feet, wrists);
- irregular shape (vertebrae);
- flat (ribs, shoulder blade).
The skeleton is the main supporting part, the frame that allows you to perform movements, stand, walk. The bones are strong, they are able to withstand high loads. With age, their fragility and fragility increases.
It happens that the bones fuse together, in some cases the protruding parts of one may enter the recess of the other.
Most of the bones in an adult are on the hands and feet, in addition, the elements are quite small.
Large department - spine and chest. The skeleton can tell a lot: experts can easily determine the age of a person, his gender and the appearance of even people who have long passed away from this life.
With an accuracy of up to 5 years, archaeologists and forensic experts are able to establish the biological age (taking into account the wear of the teeth, changes in the skeleton that occur over time).
Many people are interested in how many bones are in the human body. Let's try to answer this question.
The human musculoskeletal system consists not only of the skeleton, but also of muscles. With his help, a person makes different movements, and he also serves as protection for internal organs from various injuries. The shape of the human body is determined by the skeleton. There are about 210 bones in the body.
There are several types of bones in the human skeleton. I would like to take a closer look at how many bones are in the human body, and what they are. There are the following types:
1. long bones: brachial bone, forearm, femur and lower leg.
3. Flat: bones of the skull and scapula.
The top of the bone is covered with a dense sheath called the periosteum. Due to it, the growth of bones, their nutrition, as well as fusion in fractures occurs. Thanks to the periosteum, the bones grow in width, and in length they grow due to the division of cartilage cells, which are located between the body of the bone and its ends.
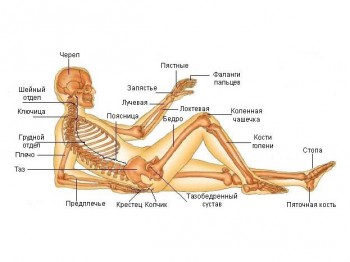
In general, the skeleton consists of the skull, the skeleton of the lower and upper limbs and the trunk.
Let us consider in more detail how many bones in the human body are in each of the components. The skull consists of the facial and cerebral sections. The brain part includes the cranium, which serves as protection for the brain from various damages. The cerebral region includes: frontal, occipital, 2 parietal and 2 temporal bones. To facial department include various small and large bones (nasal and lower and upper jaw). They are fixedly connected to each other, except for the lower jaw.
Now consider how many bones in the human body belong to the skeleton of the body. It is formed by the spine and chest. The spine consists of 4-5 coccygeal, 5 sacral and lumbar, 12 thoracic and 7. Due to this, the spine is divided into 5 sections, which have the same name as the vertebrae that they include.
The rib cage, which serves as protection for the lungs and heart from damage, consists of 12 ribs and sternum. 
The structure of the upper limbs includes three sections: hand, forearm and shoulder. The shoulder is formed by a long humerus, forearm - elbow and radius bones, and the brush consists of small bones. The arms are attached to the body with the help of the clavicles and shoulder blades, which form
The lower extremities include the feet, lower legs and thighs. The thigh consists of the femur, which is the largest in the entire body. The lower leg is made up of 2 tibia bones, and the foot is made up of several small bones, the largest of which is the calcaneus. The lower limbs are attached to the body by
Despite the data given in the article, it is still impossible to unambiguously say how many bones are in the human skeleton. For example, a newborn has much more of them than an adult, since small bones grow together into large ones already in the process of a child's growth.
Therefore, there is no specific figure reflecting how many bones in the human body. Someone indicates the number 200, someone 220.
The human skeleton is a universal framework. Bones are the hardest material in our body. The human skeleton is stronger than steel, but much lighter due to its porous structure. With a relatively small weight, the bones serve as protection for us, they act as springs when walking, jumping and running, they can stretch along with the muscles when we carry a heavy burden.
In nature, there are no such exceptionally universal frameworks as the human skeleton. Thanks to a large number and a variety of bones, a person performs complex manipulations with arms and legs, bends and unbends. Inside the skeleton is filled with bone tissue, consisting of cells and intercellular fluid rich in minerals, from above - the periosteum, thoroughly impregnated blood vessels and nourishing the bones of the body.
Bones "grow up" with the person. In childhood, for each person, they are still very elastic and resilient, they become strong only in adulthood and fragile in the elderly. Each bone performs a strictly defined function, and it is difficult for a person to even imagine what kind of load even a small bone can withstand.
Let's take a look at the bones...
There is still no exact figure on how many bones a person has. Experts say that in adulthood we should have from 206 to 208 bones. Many of them grow together with age, since a newborn has much more bones (about 350). The connective tissue that forms the fontanel of the baby, by six months passes into the bone, growing together, from it a strong cranial frame is obtained, which will perform protective function brain.
Doctors have repeatedly tried to calculate how many bones are in the human skeleton, but they have not come to a consensus. According to official data, there should be 206 bones in the human body if there are no deviations in the development of the spine, if there are no "extra" ribs (this phenomenon is not so rare in boys) and "extra" fingers and toes. In rare cases, there are additional bones on the foot. Bones can grow together only in childhood, therefore, an elderly person, as well as a young person, has the same number of bones, the last of which grows together is the clavicle, in which the formation process ends only by the age of 22-25.
Interesting to know
Despite having 350 bones, newborns do not have kneecaps. Their formation occurs only by the age of three.
The smallest bone in our body is the stirrup, which is located in the middle ear, and the largest is the femur, which is 28% of a person's height.
The coccyx is 3-5 vertebrae that grow together with age. Teeth and nails are not classified as bones, although tooth enamel is recognized as the strongest tissue in the human body.
The skeleton of a man weighs 13-14 kilograms, weight female skeleton is 9-10 kilograms - these are the average indicators of human bone mass. If we translate these data into percentages in relation to the total mass of the body, they will look like this:
- The weight of the bones of a man is 17-18% of body weight;
- The weight of the bones of a woman is 16% of the total mass;
- The weight of a child's skeleton is equal to 14% of the child's weight.
The skeleton, translated from ancient Greek as “dried”, testifies to the methods of its manufacture - drying in hot sand, or in the sun. The bone base of the human body is a unique and perfect invention of nature.
The structural features of the bones are such that they "know how" to withstand the load in the same way as a steel structure. But, if the human skeleton were "made" of steel, then it would weigh at least 200 kg and the person simply could not budge.
The individuality of the structure of bone tissue lies in the fact that it has a porous structure, due to which the skeletal mass is lightened several times, but the strength indicators, at the same time, do not change. The skeleton is the depreciation basis of the human body: with an increase in physical activity, the musculoskeletal system is able to stretch elastically and reduce pressure on other organs. The strength and plasticity of bones is due to their structure:
The skeleton of a man weighs 13-14 kilograms, the weight of the female skeleton is 9-10 kilograms.
The organic substance of bone tissue is ossein, a protein that is a type of collagen and forms the basis of bone. The bulk of inorganic substances are calcium salts, in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals, from this substance a lattice structure of bone tissue is formed. The bones of an adult and a child differ in their internal contents: in children, organic substances predominate in the bone tissue, which provide the skeleton with flexibility and elasticity, in an adult, the main component is mineral salts, which are responsible for strength.
The weight of the heaviest and lightest bones of the human skeleton
The structure of the adult human skeleton includes 206 bones, which are interconnected with the help of joints and ligaments. There are 33-34 unpaired bones, the rest of the bones are paired. The difference in number is explained by the fact that the sacral spine contains from three to five fused bones, and the number of vertebrae in cervical region may change up or down. If we assemble such a “skeletal puzzle”, it turns out that:
- there are 23 bones in the cranium;
- the spinal column consists of 26 "pieces";
- 25 bones form the body (ribs and sternum);
- the upper limbs will "compose" of 64 bones;
- it will take 62 bones to “assemble” the lower limbs.
It is interesting!
On these pages you can find out:
How much does the brain weigh
How much does a human soul weigh
How much does a sumo wrestler weigh
How much does the moon weigh
How much does the earth weigh
The skeleton of a newborn is different from that of an adult. At birth, a baby can count about 300 bones, some of them grow together at the age of up to one year, the weight of the skeleton during fetal development is almost half the mass of the embryo. After birth, a person is not completely "staffed" with the main bones. Knee cap is formed in a child only by 5-6 years of age.
The largest and heaviest human bone is the femur. This is the main “lever” that can withstand a huge load when walking and running (for compression up to 2.5-3 tons, which is much stronger than concrete!). Its length in an adult is 45 cm or more, and its weight is determined by the height of the person and the structure of the bones. The smallest bone in the human skeleton is the anvil, which is located in tympanic cavity middle ear, its length is not more than 3-4 mm, but it is one of the most important auditory bones and transmits sound vibrations to the inner ear, and the tiny formation weighs only a few milligrams.
How much does an adult human skeleton weigh?
 The weight of the skeleton of an adult will be different, depending on:
The weight of the skeleton of an adult will be different, depending on:
- gender;
- age;
- height and weight.
The bones of the female skeleton are lighter than the bones of men, due to the peculiarities of their structure. They are shorter and lighter. Archaeologists, during excavations, examining the skeleton, learned to determine to whom it belonged: a man or a woman. The common misconception that a person's weight depends on how "heavy" the bone is has no basis. Bone formations they can indeed be wider, but this does not affect the mass of a person.
To check whether a person is the owner of a "wide" bone, it is enough to measure the girth of the wrist. With indicators from 16 to 19 centimeters, the size of the bone is considered normal, over 19 centimeters we can say that you have a “wide-boned” human specimen.
Owners of large stature and large physique will have more "heavy" skeletons than fragile asthenics. A very important indicator of skeletal mass for athletes and those involved in the correction of their own weight. In order to properly distribute physical activity, the ratio of bone, muscle and fat mass of the human body is calculated.
After the age of forty, the processes of bone tissue formation change: the outer walls become thinner and more fragile, the weight of the bones decreases, and the risk of injury increases. A rather unpleasant disease of bone tissue is osteoporosis, when such a condition is diagnosed, a drug complex is prescribed to a person, a specialist prescribes a special nutrition system. At an older age, in the diet of any person, there should be a sufficient amount of dairy and sour-milk products rich in calcium, which is necessary to maintain normal bone structure. At healthy person the strength of bones is 2.5 times higher than the strength of granite, and the elasticity is comparable to oak wood. Regular physical exercise contribute to the strengthening of not only the muscular apparatus, but also increase the strength of bones.
The main skeletal mass of a person is located in the upper and lower limbs and makes up about 50% of the total mass. In the bone structure, processes of changes in the underlying tissue are constantly taking place, and within seven years, each of us becomes the owner of a “new” skeleton.
By morning, we all “grow up” a little by 0.5-1 centimeter, and by the evening we become lower. This phenomenon is connected with the fact that the fluid in the intervertebral space comes out during the day, and accumulates again during the night.
All bones in the body are interconnected, they have a movable and fixed joint. The only "independent" bone is the hyoid bone, it is not connected with other bones in any way. In its structure, the bone base of people is similar to the skeleton of a giraffe, the only difference is that the artiodactyl has a more impressive size.
Human health depends on the proper functioning of organs and life support systems. The musculoskeletal system is no exception. How healthy will be bone whether the skeleton will have sufficient weight, properly formed, depends on the ability of the body to withstand various dynamic loads. Therefore, taking care of your own health, you should not forget about the serviceability of a strong and reliable frame of the human body - the bone skeleton.