Knee pain may also be due to a form of arthritis.
The first step to treating knee pain is to get the right diagnosis. Your knee may become painful due to ligaments, tendons, muscle problems, or changes in the bone. Knee pain can also be due to one of the hundred forms of arthritis.
Symptoms of knee arthritis
To help your doctor diagnose the cause of your knee pain, it's important to pay attention to the symptoms. What are the symptoms of knee arthritis?
When is knee pain a symptom of arthritis?
The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons states that if knee pain is due to arthritis, it is likely to come on gradually and then gradually get worse. This is different from trauma, in which sharp pain knee gets better with time. With osteoarthritis, knee pain can be made worse by activities such as climbing stairs, getting up from a chair, or other movements that require you to bend your leg and put all of your body weight on your knee. In the case of rheumatoid arthritis, knee pain may be worse in the morning or worse after periods of inactivity. Rheumatoid arthritis is also characterized by periods of outbreaks and remissions. Osteoarthritis may cause pain on only one side of the body, but rheumatoid arthritis, as a rule, both knees are equally affected.
Stiffness and swelling in the knee joint
In the case of osteoarthritis, you may find that your knee becomes stiff and difficult to move. Loss of flexibility in the knee joint can be the result of a sedentary lifestyle, lack of exercise. Rheumatoid arthritis can cause swelling and inflammation in the joints. Your knee may become red and warm to the touch, and a low-grade body temperature may develop. In rheumatoid arthritis, as the disease progresses, the joint may become deformed. With both forms of arthritis, you may find that your knees are affected by the weather.
Weakness in the knee joint
According to the Arthritis Foundation, both rheumatoid arthritis and arthrosis can cause sensations such as stiffness or cracking in the knee. Your knee may become unstable, and there may be stiffness and pain in the knee joint. Arthritis can even cause you to limp if you try to relieve pressure on your knee.
How do you know if knee pain is caused by arthritis?
Knee pain can be caused by many reasons. You may have damage to the tendons, ligaments, and muscles surrounding the knee joint. Knee pain can also be associated with a form of arthritis. The only way to find out the cause of knee pain is to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Tests can help determine the cause of your knee pain.
First of all, the doctor will look at your symptoms: What kind of pain are you experiencing? What makes pain better and what makes it worse? The doctor may look for signs of stiffness, swelling, and redness, which may indicate arthritis. If you have pain in one knee, then osteoarthritis can be suspected; pain in both knees most likely indicates rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis knee pain tends to get worse after periods of inactivity and improve with movement. In this way, it may differ from ligament or tendon injuries, which worsen with movement. In addition, arthritis can cause generalized pain, while tendon or ligament damage can result in very localized pain.
X-rays will be taken to help identify changes in the bone that indicate arthritis. Osteoarthritis, one of the most common forms, is caused by wear and tear on cartilage in the knee. When this happens, the bones rub against each other, which can lead to the development of a bone spur. X-ray is the most informative test to confirm the diagnosis of osteoarthritis. It may show narrowing of the space between the bones (indicating that the cartilage is thinning), as well as changes in bone tissue(like a spur). If your doctor does not see changes on the x-ray, they may order an MRI test that shows injury to the surrounding soft tissues and can help rule out arthritis as the cause of knee pain.
Need blood tests. If you are diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, you will need additional blood test results to determine if knee pain is related to arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis is autoimmune disease, which causes inflammation of the articular bag. A blood test can show active inflammation and other factors that are present in this disease (See article:). In rheumatoid arthritis, a blood test will likely show low red blood cells, high white blood cells, and elevated level platelets. In addition, your doctor may take a fluid sample from your knee, which can help confirm a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
How to relieve arthritis knee pain?
If you are suffering from pain in one or both knees due to arthritis, then you should know that there are ways to relieve the pain. There are many forms of arthritis that affect each person differently. Therefore, you may even need to try a combination of methods and approaches to relieve knee pain and stay active.
- Need to lose weight! The lower your body weight, the less stress on the knee joint. The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons claims that weight loss reduces the load on weight-bearing joints (like the knee joint). Losing weight can help reduce pain and improve joint function, especially when walking. Losing just 7.5 kg of body weight can reduce knee pain by 50% (according to a recent study presented at the American College of Rheumatology; X Annual Scientific Meeting). Aerobic or cardiovascular exercise is the best way to lose weight. So walk, ride a bike, swim and dance. To successfully lose weight, a person needs to do 30 to 45 minutes of aerobic exercise at least three to five days a week. These 30-45 minutes can even be broken up into shorter segments throughout the day if needed.
- Do it regularly physical exercises. Exercise is an important part of knee arthritis treatment. Stretching and flexibility exercises can help reduce stiffness in the knee joint. Strengthening the muscles of the thighs and legs will relieve pressure from knee joint. Squats, lunges, etc. are useful. The National Institute on Aging believes that exercise strengthens muscles, and that strong muscles support and protect joints. If exercising on the ground is too difficult for you, do exercises in the water. Do exercises that don't put pressure on your knees. It is important to remember that people with rheumatoid arthritis should not exercise on the days of the outbreak.
- Use assistive devices and supports. Using a cane, crutch, or brace can also help arthritis in the knee. If you only have arthritis in one knee, use a cane or crutch in your opposite hand. Using a cane in the same hand as the affected knee will cause you to lean too heavily on the affected side. Also, talk to your doctor about which type of brace is best for you. A brace can help maintain proper knee alignment, which can help reduce your symptoms.
- Have your doctor prescribe treatment for arthritis. There are medications that are effective for treating knee arthritis. However, the lifestyle changes listed above are still necessary. According to the National Institutes of Health, lifestyle changes without medication are preferable for osteoarthritis and other forms of joint inflammation. If necessary, drugs should be used in addition to lifestyle changes. Doctors usually prescribe pain medications, anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, and muscle relaxants. In addition to drug treatment good for knee arthritis is the use of hot and cold therapy.
- Consider having surgery. In cases where knee arthritis causes severe symptoms or significantly affects your daily life, you may need surgery to relieve symptoms. There are many types of knee surgery, including knee replacement options. Talk to your doctor about how much surgery you need.
Never ignore knee pain! Without adequate treatment, the injury, inflammation, and pain in the joint can develop into a more severe condition. The sooner you start treatment, the better your chances of a speedy recovery will be. See your doctor for a correct diagnosis. Only establishing the exact cause of your knee pain will help you find the right approach to manage your symptoms. Remember that knee arthritis is not a death sentence! There are methods that can help relieve knee pain and drugs that a doctor prescribes to treat knee arthritis.
Osteoarthritis of the knee, like other types of arthrosis, is best treated if it is started on early stage. The success of treatment depends on the correct diagnosis, and the symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint are sometimes mistaken for symptoms of other diseases. Even a specialist cannot always deliver accurate diagnosis based on the patient's complaints and the results of a physical examination (examination, palpation). It is necessary to pass tests, undergo an instrumental examination.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint is associated with the destruction of cartilage tissue, therefore it is extremely important to start taking chondroprotectors from the moment the first symptoms appear. If, instead, the pain is relieved with pills and rubs, the cartilage destruction will progress and become irreversible.
Pathogenesis and symptoms
With gonarthrosis, the symptoms increase gradually, and often patients do not consider periodic pain in the knees and stiffness of movements is sufficient reason to see a doctor. When, finally, the patient comes to a specialist, he diagnoses arthrosis of the 2nd degree. Some people seek help only at stage 3 of the disease, when conservative treatment practically no effect. Knowing the symptoms of gonarthrosis of the knee joint will help to avoid such a situation by sounding the alarm in time.
Signs of osteoarthritis of the knee:
- pain ranging from moderate and episodic in the early stage to intense and constant in the later stage. If at first the pain is localized in the knee area, then over time it covers the entire leg;
- crunch, clicks during flexion-extension of the leg at the knee;
- stiffness of movements, turning into a limitation of joint mobility;
- swelling, swelling of the knee;
- deformation of the knee joints.
Knee arthrosis can be unilateral or bilateral. In primary arthrosis associated with age-related changes, both joints are usually affected, in secondary, especially post-traumatic, one joint.
The causes of arthrosis are varied: trauma, systematic excessive stress on the joints, autoimmune, endocrine, metabolic disorders. But the mechanism of the development of the disease in all cases is the same, as well as the symptoms. Only the development of post-traumatic arthrosis can immediately begin with acute manifestations, in other cases, the increase in symptoms stretches for a couple of years.
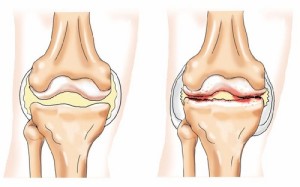
First, the properties of cartilage tissue change, the cartilage becomes less elastic, dries out, becomes cloudy and begins to crack. The shock-absorbing pad between the bones becomes thinner, and their friction against each other is accompanied by pain. Often an inflammatory process develops in the synovial membrane - synovitis. The volume of the joint fluid increases, the knee becomes like a ball, the temperature may rise. Cartilage destruction leads to bone deformity, appearance on the periphery articular surfaces osteophyte outgrowths. Deforming osteoarthritis (DOA) is manifested by intense pain, muscle spasms, and a change in the contour of the joint is striking. Acute pain syndrome, muscle spasm and mechanical obstacles in the form of osteophytes severely limit the mobility of the limb.
Diseases with similar symptoms
Pain in the knees is characteristic of a number of other diseases, so you need to focus on the totality of symptoms, the results of tests, imaging diagnostics. At differential diagnosis osteoarthritis should take into account the following points:
- if the meniscus is damaged, the pain is severe, accompanied by a crunch, appears immediately after an awkward movement, but after about a quarter of an hour it subsides, and the next day edema develops;
- inflammation of the knee tendons (tendonitis) is manifested by pain with active movements and palpation, crunching, joint stiffness, there are signs inflammatory process- redness of the skin, local fever, swelling. The diagnosis is specified by means of ultrasonography;
- with arthritis, a blood test reveals an inflammatory process;
- pain associated with vascular diseases, have a specific character, which is usually described by the words "turning the knees." Such pains are always symmetrical;
- to exclude tuberculosis of the knee joint, it is necessary to perform a biopsy of the synovial membrane;
- hydrarthrosis (dropsy of the joint) resembles arthrosis complicated by synovitis, but studies do not reveal an inflammatory process, changes in the bone and cartilage tissue of the joint;
- Articulating bone tumors are ruled out by X-ray.
Secondary arthrosis of the knee can develop against the background of arthritis, gout, ankylosing spondylitis, varicose veins veins. Therefore, it is important not to miss the moment when manifestations of arthrosis itself join the symptoms of the cause of the disease.
Diagnostics
Clinical signs of DOA of the knee joint are quite expressive, bone growth is visible without X-ray, the leg deviates from the normal axis. With bilateral gonarthrosis, an X-shaped (valgus) or O-shaped (varus) deformity of the limbs is formed, the gait changes. At stage 2, you can already notice the coarsening of the contours of the joint. But arthrosis of the 1st degree does not have pronounced external signs, it is manifested by starting pains, stiffness of the joints in the morning, with the development of synovitis - swelling.
This set of symptoms allows an experienced specialist to suspect osteoarthritis of the knee joint, but not to make an unequivocal diagnosis with certainty. Therefore, in case of arthrosis of the knee joint, the diagnosis should not be limited to examination and questioning of the patient.
To confirm the diagnosis of gonarthrosis will help:
- radiography;
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Tests are prescribed to exclude other diseases with similar symptoms, primarily arthritis. With arthrosis, general and biochemical analysis blood does not reveal abnormalities, and a slight increase in ESR indicates synovitis.
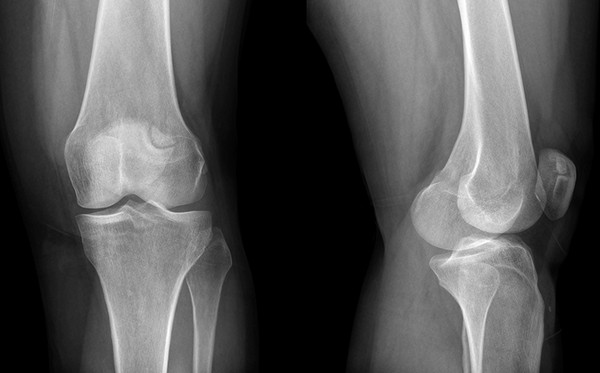
Radiography is the main method for diagnosing gonarthrosis, the medical history necessarily includes a number of images taken at different stages of the disease. If the development of arthrosis has just begun, the x-ray may not show changes, and later on the picture shows:
- narrowing of the gap between the articulating bones;
- compaction of the subchondral bone (bone plate located directly under the articular cartilage);
- expansion of the articular ends of the bones;
- sharpening of the edges of the condyles;
- spike-shaped osteophytes;
- loose foreign bodies (particles of destroyed cartilage) in the articular cavity.
In older people, x-rays can show a number of changes from this list, but there are no symptoms characteristic of osteoarthritis of the knee. Therefore, arthrosis cannot be diagnosed on the basis of an X-ray examination alone; clinical signs must be taken into account.
In case of arthrosis of the knee joint, a polypositional radiography is required. At a minimum, pictures are taken in frontal and lateral projections; to obtain more accurate and detailed information, they resort to oblique, axial and other projections. This requirement is associated with the structural complexity of the knee joint and the possibility of localizing the degenerative-dystrophic process in a limited area, which is visible only when shooting at a certain angle.
Other methods of hardware diagnostics
Changes in bone tissue develop in a certain sequence, therefore, with the help of an x-ray examination, it is possible to accurately determine the stage of arthrosis. But this method does not allow to visualize changes in soft tissues, ligament-meniscal complex. Therefore, it is supplemented ultrasound diagnostics, tomography.
The ultrasound shows:
- thinning, destruction of articular cartilage;
- meniscus damage;
- a change in the volume of the joint fluid (its increase is a sign of arthritis or arthrosis complicated by synovitis, but the absence of an increase in volume clearly indicates arthrosis).
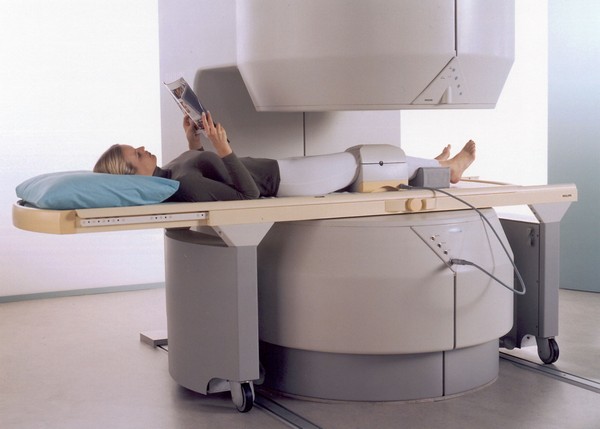
Ultrasound is an insufficiently accurate diagnostic method, the reliability of the results largely depends on the qualifications of the specialist who conducts the examination. CT and MRI are more informative. CT scan allows you to assess the condition of bones, cartilage and menisci, ligaments and tendons, to see in detail the contents of the joint capsule. MRI is the most expensive, but the most accurate and informative diagnostic method, thanks to which it is possible to identify specific changes at the stage of the first clinical manifestations. In particularly difficult cases, they resort to arthroscopy - a miniature camera is inserted into the joint through a small incision.
The insidiousness of gonarthrosis lies in the weak severity of symptoms at a stage when the development of the disease can still be slowed down. If you are worried about knee pain that occurs at the beginning of the movement, but soon disappears, and in the morning it takes some time to “disperse”, overcome stiffness, you should be alert and consult a doctor. Only a rheumatologist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe proper treatment, which will help to maintain motor activity for many years, avoiding disability. Early diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the knee joint is the key to effective treatment.
Among all forms of articular pathology, a special place is occupied by osteoarthritis of the knee joint, the treatment of which is one of the central problems not only of rheumatology, but of the whole modern medicine. This is due to the wide spread of the disease and the objective risk of severe complications, up to the disability of patients.
The disease is marked by damage to the cartilaginous tissue of the knee due to an imbalance in the process of its renewal. Natural restoration ceases to compensate for the course of tissue destruction, as a result of which the cartilage becomes thinner and does not perform its function in the right amount. (the second name of the disease) is an organ pathology. The entire joint is involved. His condition is characterized by progressive stiffness and deformity.
How to notice this disease?
Morning stiffness in the knee joint may indicate the onset of osteoarthritis
The leading symptom of the disease is pain. It is she who causes the patient to see a doctor and is the main cause of disability. At the same time, there is no clear correlation between the severity of pain and various destructive changes.
Another important sign of the disease, which can sometimes be more indicative of pain, is the limitation of the mobility of the affected knee. Morning stiffness of the limb can reach 30 minutes. With the development of the disease, this symptom is fixed and acquires regular stability.
An additional sign of gonarthrosis is characteristic (crepitus). Not those slight clicks that occur with healthy people, but a rough crunch that accompanies the movement of diseased joints.
X-ray examination shows the presence of bone growths in the joint - osteophytes, which are formed at a certain stage of the disease. There are four such stages when pathologies are fixed on the x-ray:
- doubtful changes in the joint;
- minimal changes, narrowing of the joint space;
- moderate distinct changes;
- pronounced pathology.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee
With deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint, the treatment regimen is determined by several basic principles:
- reduction of pain syndrome;
- improvement of joint function;
- preventing the development of disability.
In addition, much attention is paid to educational work with patients. The ability of the patient to live with arthrotic pain, to properly use the load on the joints, to correctly apply medications are important components. successful treatment and improving the quality of life.
Relief of pain
An important task in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee is to minimize the use of drugs with side effects.
To reduce pain in gonarthrosis, there is a large number of methods, but the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is of primary importance. Widely known standard preparations: aspirin, diclofenac, ibuprofen, piroxicam, etc. They well suppress inflammatory and pain reactions, but can cause side effects large spectrum: from gastrointestinal to platelet. Therefore, when prescribing these drugs, clinical and laboratory monitoring is mandatory.
An important goal of treatment is to minimize the use of drugs with an undesirable effect. In this regard, their use is combined with local therapy. Application nonsteroidal drugs in the form of creams, gels can significantly reduce pain and reduce the need for oral administration of the drug. This is an important aspect of long-term treatment. However, anti-inflammatory drugs only remove the main symptoms - pain and inflammation, but they do not treat the disease itself. If limited only to them, the disease will progress to its most severe stage.
Intra-articular treatment
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint requires systemic treatment with drugs that slow down the development of the disease. They should be taken for a long time. These are symptomatic slow-acting drugs. The effect of their use develops after a few months from the start of the reception. However, their action continues for a long time even after drug withdrawal.
We are talking about chondroprotectors - drugs that nourish the articular cartilage and prevent its destruction. These include: chondroitin sulfate (Struktum), glucosamine sulfate (Dona) and combined means such as Teraflex or Artra. These disease-modifying drugs are selected by the doctor individually for each patient. They help especially well in the first and second stages of the disease.
Drugs are widely used in the treatment of gonarthrosis hyaluronic acid. They belong to non-drug therapy, as they do not have a systemic effect. In fact, these are synovial fluid prostheses. They replace it in the affected joint. This reduces pain and significantly improves joint mobility. The effect can last up to 8 months. Drugs are injected into the joint, 3-5 injections with a weekly interval.
In the critical stage of the disease, when the function of the joint is lost to a very large extent, and pain syndromes are not amenable to relief traditional means, apply surgical methods treatment. The problem is solved by endoprosthetics of the joint. Damaged surfaces are replaced with a biocompatible prosthesis that provides painless, smooth knee movement.
Currently, osteoarthritis of the knee has good prospects for treatment without cardinal surgery. By creating new drugs that affect various processes of the pathogenesis of the disease. And spectrum medicines, to get rid of this heavy suffering, is steadily expanding.
